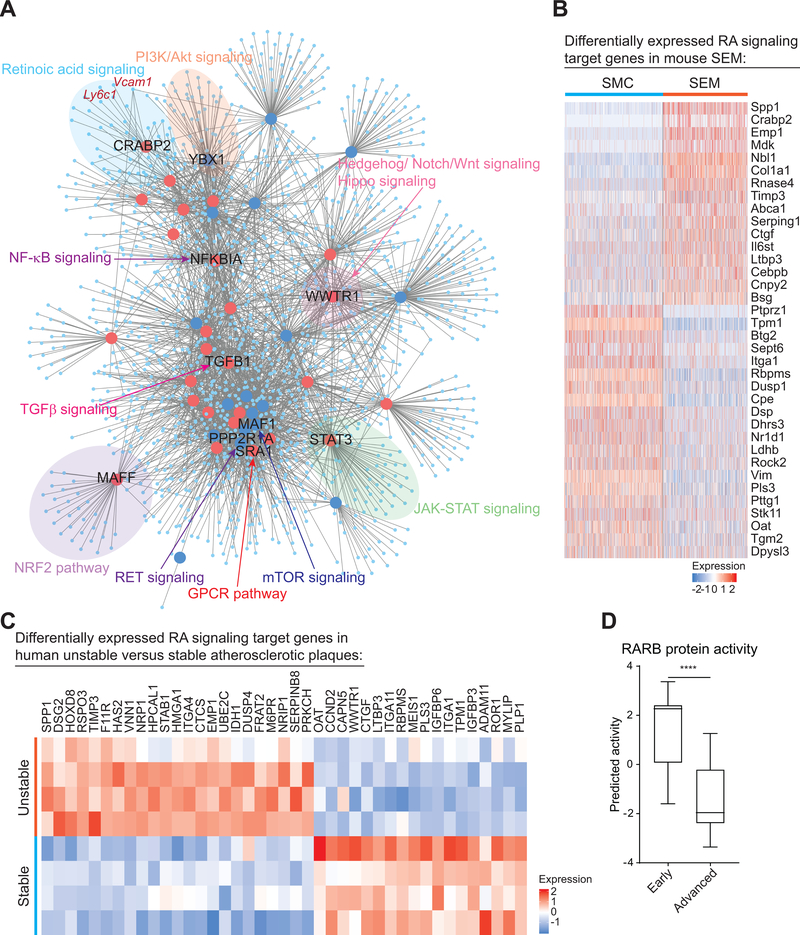
Figure 4. metaVIPER analysis identifies multiple master regulators of SMC to SEM cell transition during atherosclerosis, among which RA signaling is also found to be dysregulated in human atherosclerosis development and progression.
A, ARACNe network showing top 50 activated (red large dots) and repressed (blue large dots) MRs and their predicted target genes (light blue small dots) identified via metaVIPER using ZsGreen1+ scRNA-seq data of Ldlr−/− mice fed 16-week WD. Some MRs-involved canonical cell signaling pathways are highlighted. Vcam1 and Ly6c1, in dark red text, are shown as predicted target genes of CRABP2, a transducer of retinoic acid (RA) signaling. B, Heatmap showing significantly up and downregulated (fold change ≥ 1.2, Bonferroni corrected P-value < 0.05) RA target genes (36 genes) in SEM cells relative to SMC. C, Heatmap showing 41 RA signaling target genes that were differentially expressed (fold change ≥ 1.2, FDR adjusted P-value < 0.05) in human unstable plaques (visible zone of plaque rupture) of atherosclerotic carotid arteries compared to stable plaques (macroscopically normal adjacent areas). Paired unstable and stable plaques were from 4 individual patients30. D, Predicted protein activity of RA signaling transducer, RARB (retinoic acid receptor beta), in early (intimal thickening and xanthoma, n=13) and advanced (fibrous cap atheroma, n=16) human atherosclerotic lesions of carotid arteries31. Protein activity was estimated using metaVIPER. Values are shown as box and whisker plot (min to max). ****P < 0.0001.