Figure 2. Mechanisms of BAP1 activity in cancer development.
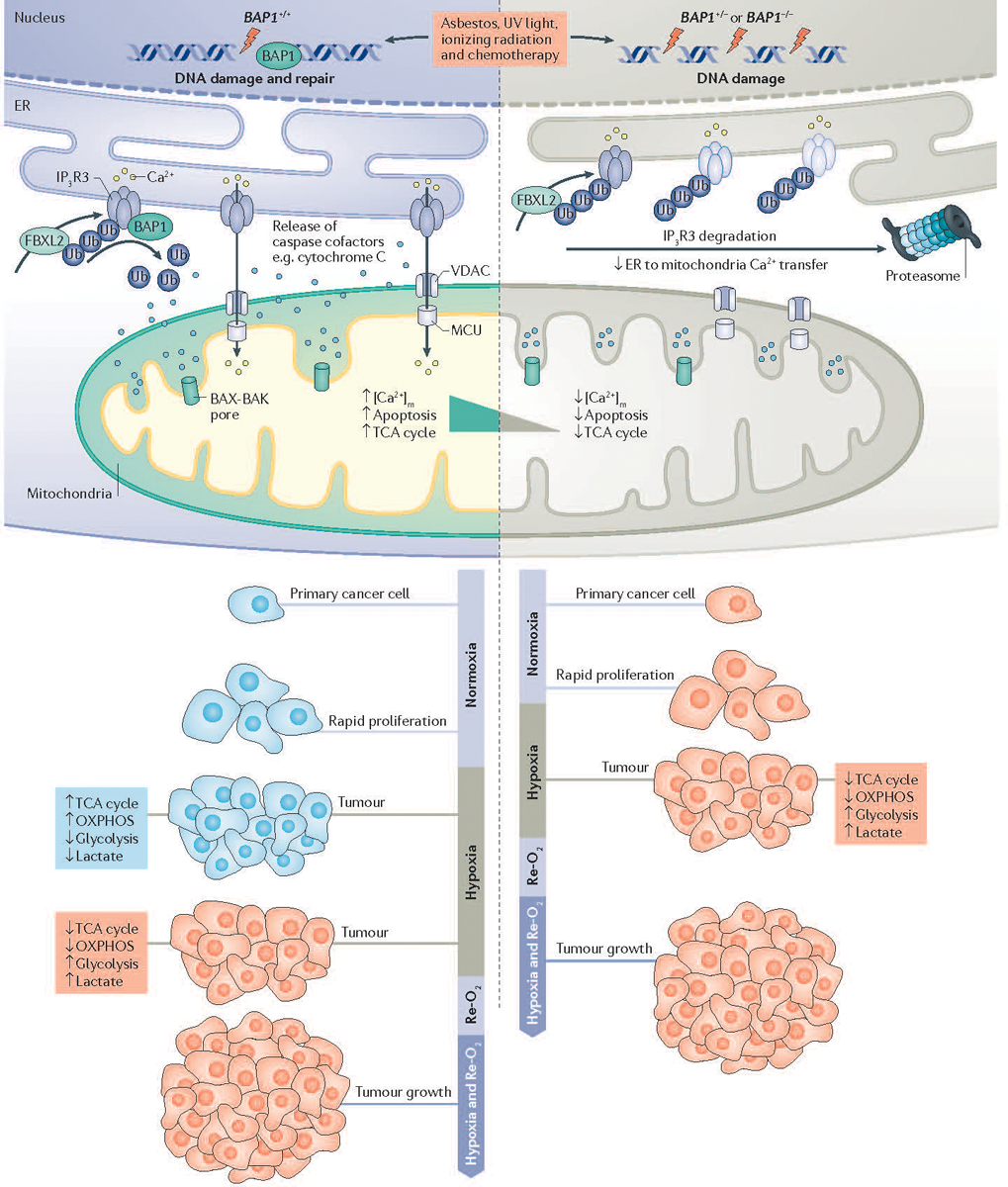
The powerful tumor suppressor activity of BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1) and its ability to regulate gene x environment interactions (GxE) in carcinogenesis are related to its dual role in the nucleus, where BAP1 contributes to DNA repair by modulating homologous recombination (HR), and in the cytoplasm where BAP1 regulates cell death and mitochondrial respiration30. In the cytoplasm, BAP1 localizes at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) where it binds, deubiquitylates (following F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 2 (FBXL2) ubiquitylation), and stabilizes type 3 inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R3), modulating calcium ion (Ca2+) release from the ER into the cytosol and mitochondria, and thus promoting apoptosis30. In primary cells exposed to either asbestos, ionizing radiation (IR) or ultraviolet (UV) radiation, reduced levels of nuclear BAP1 impair DNA repair. At the same time, reduced cytoplasmic BAP1 levels impair apoptosis, increasing the fraction of cells that survive DNA damage and that over time may become malignant30. In addition, mitochondria need Ca2+ for aerobic oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). In response to tumor hypoxia, cancer cells need to adjust their metabolism from aerobic (blue) to glycolytic (red) in order to sustain growth and survival. Primary cells from BAP1+/− individuals have reduced mitochondrial OXPHOS and increased aerobic glycolysis and lactate production, even in the presence of oxygen, a phenomenon known as the ‘Warburg effect’56. Therefore, the ‘Warburg effect’ in addition to being a hallmark of cancer cells is also found in normal cells from BAP1-mutant carriers, and contributes to the adaptation to metabolic stress during tumorigenesis56. BAP1+/+, cells with BAP1 wild-type; BAP1+/−, cells with heterozygous BAP1 mutations, containing about 50% of BAP1 protein levels compared to wild-type cells30. [Ca2+]m, mitochondrial calcium; MCU, mitochondrial calcium uniporter; Re-O2 reoxygenation; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; Ub, ubiquitin; VDAC, voltage-dependent anion channel.
