Fig. 4. PfAvr4-2 can disrupt existing Ca2+-mediated cross-links formed between adjacent homogalacturonan chains.
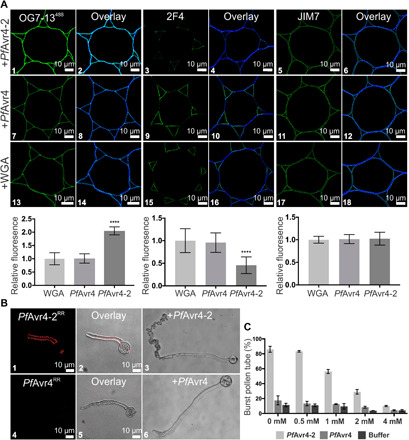
(A) Labeling of cross sections of Arabidopsis stems with the OG7-13488 probe and the 2F4 and JIM7 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) after pretreatment of the stems with 10 μM PfAvr4-2, PfAvr4, or WGA. The OG7-13488 probe is conjugated to the green fluorophore Alexa Fluor 488, whereas a secondary mAb also conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 was used for detecting the 2F4 and JIM7 mAbs. Cells are pith parenchyma. Labeling with the OG7-13488 probe necessitates the addition of 1 mM Ca2+ in the labeling buffer. Bottom graphs show the fluorescence intensity of the OG7-13488 probe, the 2F4, and JIM7 mAbs, relative to WGA (signal set to 1.0). Error bars indicate SD (OG7-13488, n = 15; 2F4488, n = 20; JIM7, n = 12). Statistical differences between PfAvr4-2 and other treatments were determined by ANOVA using Tukey’s test. ****P < 0.0001. (B) Microscope images of germinating pollen tubes of tomato incubated at increasing calcium concentrations ([Ca2+]) with PfAvr4-2RR or PfAvr4RR conjugated to the red fluorochrome Rhodamine Red (RR). Shown are the images where 1 mM CaCl2·2H2O was used in the labeling buffer. (C) Effect of PfAvr4-2, PfAvr4, and a buffer control under increasing [Ca2+] on bursting of tomato pollen tubes. The experiment was repeated in triplicate, and 100 pollen tubes were counted in each of the replicates. Error bars indicate SD from three replicates.
