Fig. 8. PfAvr4-2 enhances the activity of fungal endo-PGs.
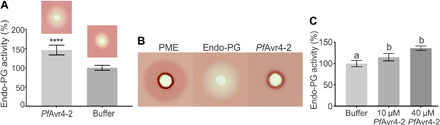
(A) Relative quantification of fungal endo-PG activity in the presence of PfAvr4-2 using the PECTOPLATE. The bar graph shows relative quantification based on the intensity of Ruthenium Red staining around the inoculation wells of endo-PG activity when the enzyme is applied alone or in a mixture with PfAvr4-2. Experiments were done in triplicate, and the intensity of the fuchsia-colored halo produced by the activity of the endo-PG is set to 100%. Error bars indicate SD from the three experiments. Student’s t test was used to evaluate statistical significance of the difference between the two treatments. ****P < 0.001. The images above the bars provide a visual representation of the results. (B) Visual representation of the PECTOPLATE radial diffusion assay used to compare the pectin-related enzymatic activity of PME, endo-PG, and PfAvr4-2. The enzymatic activity of the three pectin-related proteins is assessed on the basis of the size of the fuchsia-stained haloes in the PECTOPLATE. (C) Relative quantification of endo-PG activity in the presence of increasing amounts of PfAvr4-2. The enzymatic activity of endo-PG was monitored by measuring using 2-cyanoacetamide, the amount of oligogalacturonides (OGs) released in the buffer. The activity of endo-PG alone was set to 100%, and the activity of the enzyme in mixtures with different amounts of PfAvr4-2 was expressed relative to this activity. Experiments were done in triplicate, and error bars indicate SD. Treatments with the same letter were not significantly different by a Tukey’s test (α = 0.05).
