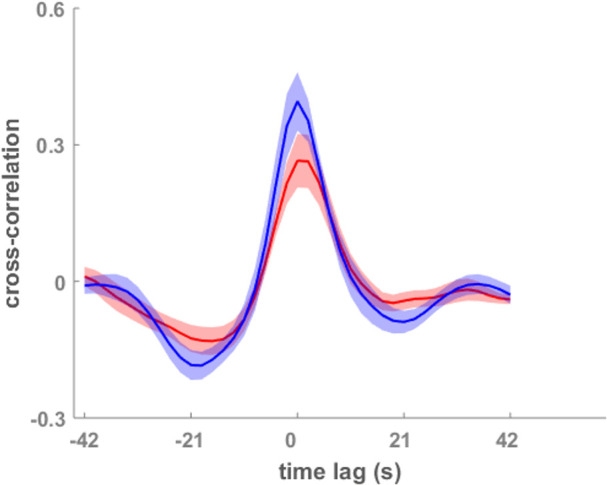
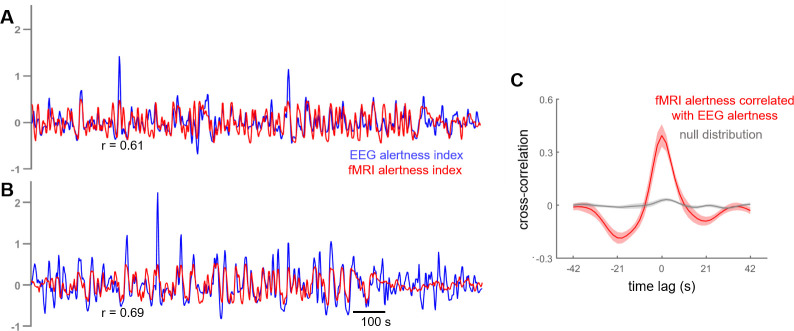
Figure 2. Cross-correlation between estimated fMRI alertness index and measured EEG alertness index.
(A, B) fMRI alertness index (red), superimposed on the EEG alertness index (blue), for two example scans. Note that the EEG data from these scans was not used in the creation of their fMRI alertness time courses, and are only used to evaluate the ability of the fMRI alertness index to track electrophysiological arousal. (C) Temporal cross-correlation between the fMRI alertness index and EEG alertness index (mean ± SE, n = 12 scans; red) together with a null distribution (gray) constructed for statistical comparison (see Materials and methods).
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Further analysis of the reliability and across-subject generalizability of the alertness estimation approach.
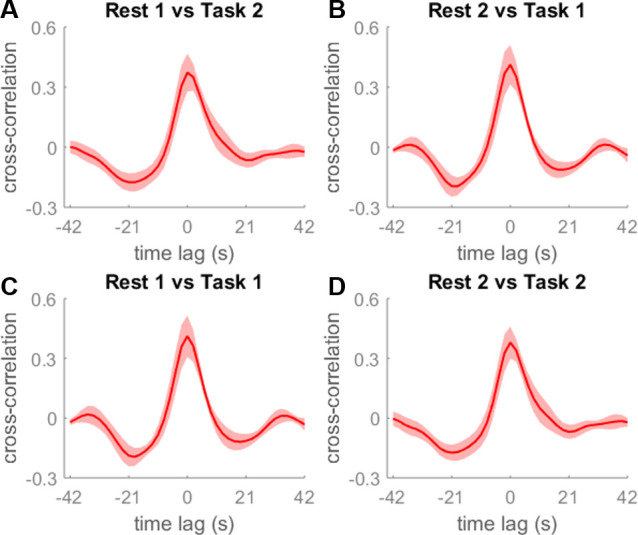
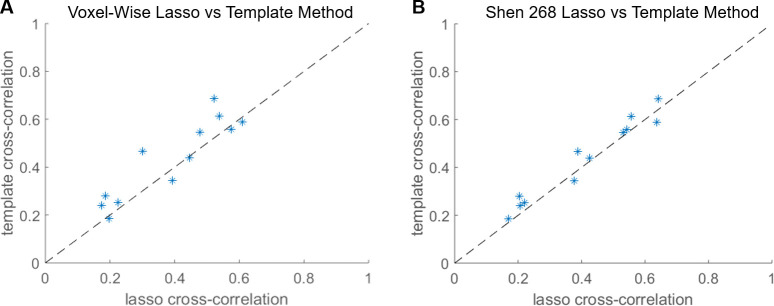
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Lasso regression model for alertness prediction.
Figure 2—figure supplement 3. Model performance when trained on task data and tested on resting-state data.