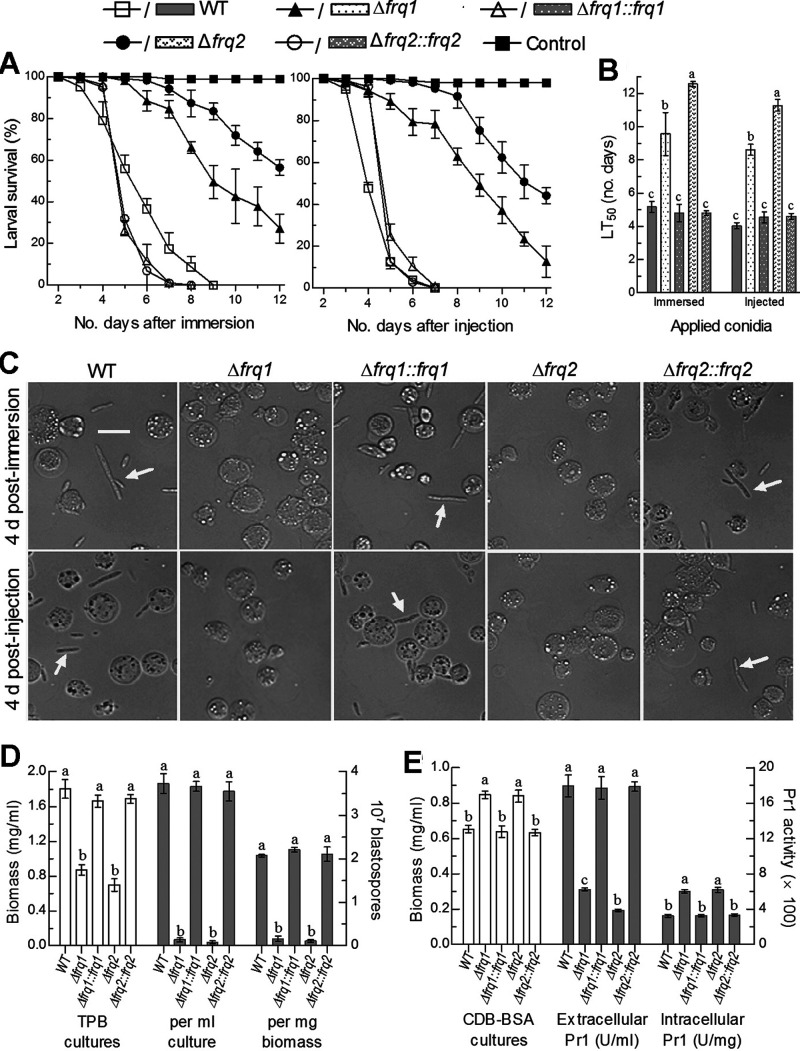
FIG 1.
Requirements of frq1 and frq2 for the virulence and virulence-related cellular events of B. bassiana. (A) Survival trends of G. mellonella larvae after immersion in a 107 conidia/ml suspension for normal cuticle infection and injection with ∼500 conidia per larva for cuticle-bypassing infection. (B) LT50 estimates (in days) for the resultant time-mortality trends of different fungal strains against the larvae. (C) Microscopic images (scale bar, 20 μm) of hyphal bodies (arrowed) and host hemocytes (spherical or subspherical cells) in the hemolymph samples taken from the larvae surviving 4 days after immersion and injection. (D) Biomass levels (white bars) of fungal strains in the 3-day-old cultures of a 106 conidia/ml TPB shaken at 25°C and blastospore yields (gray bars) per milliliter of TPB culture or per milligram of biomass (dimorphic transition rate). (E) Biomass levels (white bars) of fungal strains in the 2-day-old cultures of a 106 conidia/ml CDB-BSA shaken at 25°C and extra- and intracellular Pr1 activities (gray bars) quantified from the supernatants and protein extracts of the cultures. Different lowercase letters in each bar group denote significant differences (Tukey’s honestly significant difference [HSD], P < 0.05). Each error bar indicates standard deviation of the mean from three independent replicates.