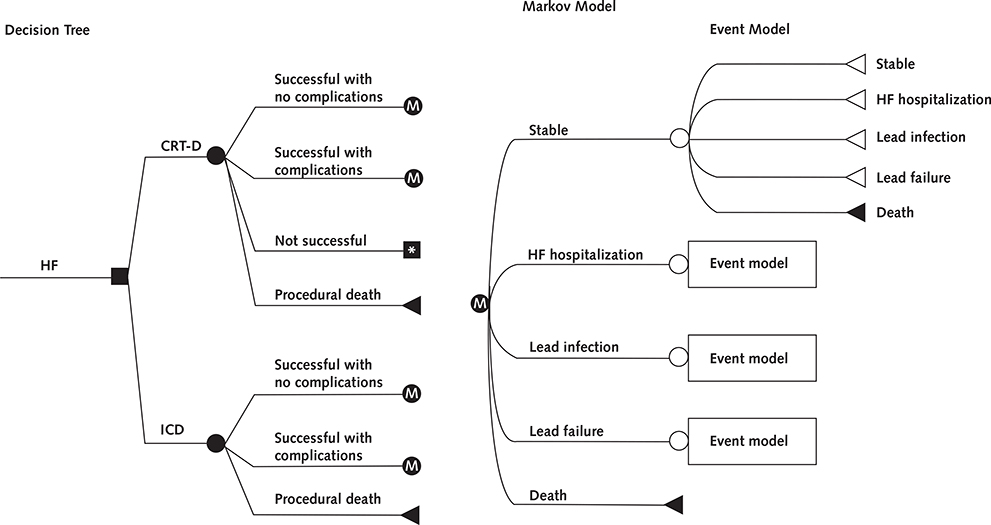
Figure 1.
Decision tree and Markov model.
The square represents the choice between the implantation of an ICD or CRT-D, whereas the circles represent chance nodes. Patients who receive a device can have a successful implantation with or without complication or die during the procedure. Patients assigned to receive CRT-D can further have an unsuccessful implantation, in which case they will receive an ICD. Patients surviving implantation enter the Markov model (assigned “M”), which represents the clinical events that can occur during each 30-day period until the patient dies. CRT-D = cardiac resynchronization therapy combined with an ICD; HF = heart failure; ICD = implantable cardioverter-defibrillator.
* Remains in CRT-D cohort but receives ICD with same outcomes/risks as “ICD successful with no complications” group.