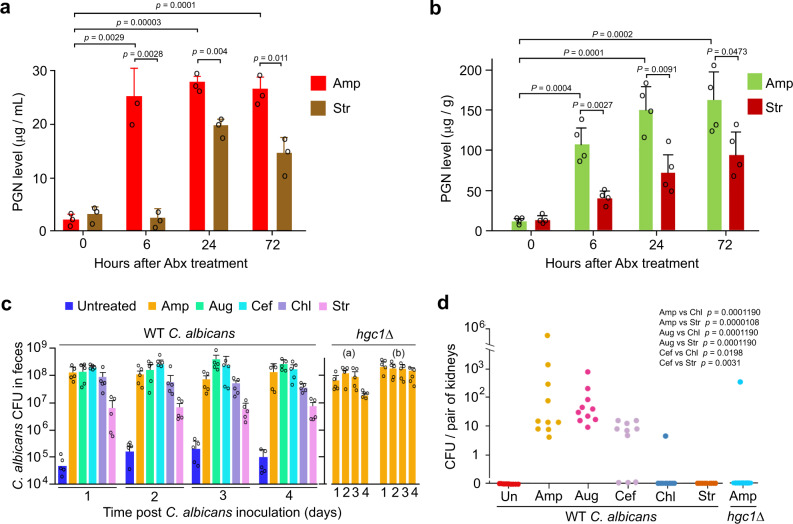
Fig. 6. β-lactam antibiotic treatment promotes C. albicans dissemination in mice.
a ELISA quantification of PGN in the lumen of the cecum. Mice (n = 3) were sacrificed at the indicated time to harvest the cecum, which was cut open and put into 1 mL of PBS to elute the intestinal content. The eluant was centrifuged at 10,000 g for 10 min, and the supernatant was collected for PGN quantification by ELISA. b PGN in the feces of mice (n = 4) treated with Amp or Str was quantified using the HEK-Blue NOD2 tlr5-/- cell assay. c C. albicans (WT and hgc1Δ/Δ) CFU in the feces of mice (n = 5) treated with different antibiotics. hgc1Δ (a) and (b), mice were inoculated with 1 × 108 and 2 × 108 C. albicans yeast cells, respectively. d CFU / kidney of WT C. albicans and the hgc1Δ/Δ mutant (+ARG4 +HIS1 +URA3) in the kidney of mice (n = 10) treated with different antibiotics. P values in (a) and (b) were determined using two-tailed unpaired t test. P values in (d) were calculated using Fisher’s exact test with odd 95% confidence intervals and alternative = two side in a 2 × 2 contingency table with df = 1. Error bars are means ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.