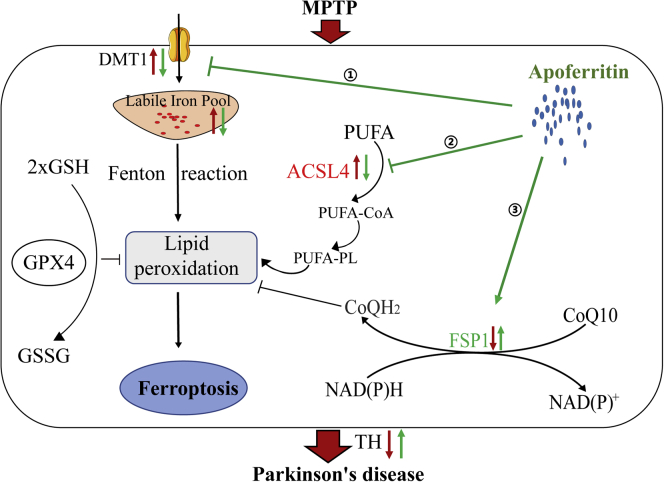
Figure 6.
A model of the possible mechanisms underlying the neuroprotective effect of apoferritin against MPTP
MPTP might result in the degeneration of DA neurons through the following pathways: (1) The increase of DMT1 in the SN leads to an increase in iron uptake, which increased the production of ROS by the Fenton reaction, resulting in lipid peroxidation. (2) The increased expression of ACSL4 protein in the SN results in the activation of PUFA, which further aggravates lipid peroxidation. (3) The decreased expression of FSP1 in the SN results in a decrease in the regeneration of reduced CoQ10, which traps lipid peroxidation free radicals, thus leading to ferroptosis. The effect of apoferritin is to abolish the increase in DMT1 and ACSL4 induced by MPTP, and to up-regulate the expression of FSP1 to inhibit lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. The red arrow represents the changes induced by MPTP, and the blue arrow represents the effect of apoferritin pretreatment.