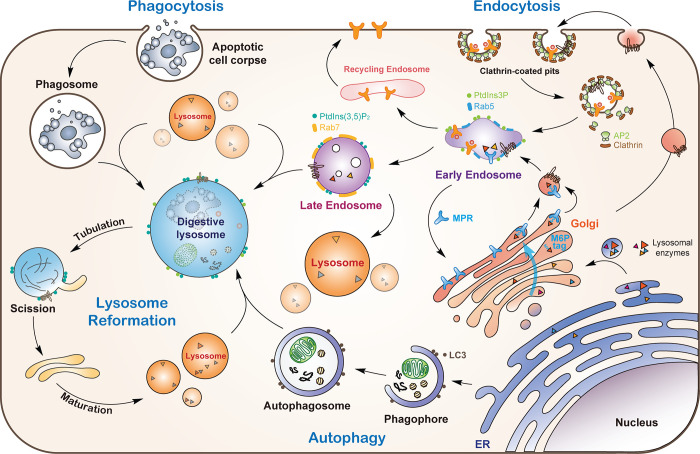
Figure 1.
Lysosomes receive proteins and cargos from multiple pathways. Lysosomal hydrolases are synthesized and modified by linkage with oligosaccharides in the ER and transported to the Golgi apparatus. Following recognition of the mannose residues in the oligosaccharide chain by MPR, the hydrolase–MPR complexes are delivered to early endosomes. Newly synthesized lysosomal membrane proteins are either sorted at the TGN and delivered to endosomes (direct pathway) or first delivered to the plasma membrane and then endocytosed to reach early endosomes (indirect pathway). Receptors not destined for lysosomes are recycled back to the plasma membrane or Golgi. Early endosomes undergo a conversion to late endosomes, which then fuse with lysosomes. Phagocytosed cargos are enclosed in phagosomes, which undergo a maturation process and fuse with lysosomes. Autophagic cargos are delivered to lysosomes by fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes. Lysosomes reform from digestive lysosomes (endo-, phago-, and autolysosomes) by tubulation and scission to form protolysosomes, which mature into functional lysosomes.