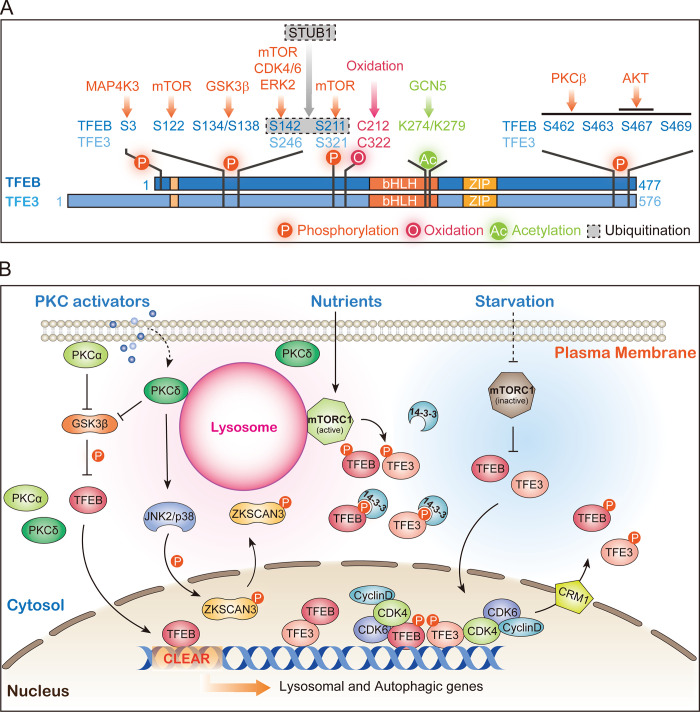
Figure 3.
TFEB/TFE3-dependent lysosome biogenesis. (A) Regulatory modifications of TFEB/TFE3. TFEB/TFE3 are phosphorylated (orange arrows), acetylated (green arrow), and ubiquitinated (gray arrow) by the indicated enzymes. Direct oxidation by reactive oxygen species can also occur (red arrow). (B) mTOR-dependent and PKC-dependent lysosome biogenesis pathways. Under nutrient-rich conditions, TFEB/TFE3 is phosphorylated by lysosome-localized mTOR. Phosphorylated TFEB/TFE3 bind to 14-3-3 proteins and are sequestered in the cytoplasm. With starvation, mTOR is inactivated and unable to phosphorylate TFEB/TFE3, leading to their nuclear translocation and activation. Activation of PKC leads to phosphorylation and inactivation of GSK3β, which then fails to phosphorylate TFEB, thereby inducing nuclear translocation of TFEB. Activated PKC induces JNK2/p38 activation, which phosphorylates ZKSCAN3 and leads to its cytoplasmic translocation and de-repression of lysosomal genes. Nuclear TFEB/TFE3 are rephosphorylated by CDK4/6 (and probably also by mTOR and GSK3β) and relocate back to the cytoplasm in a CRM1-dependent manner.