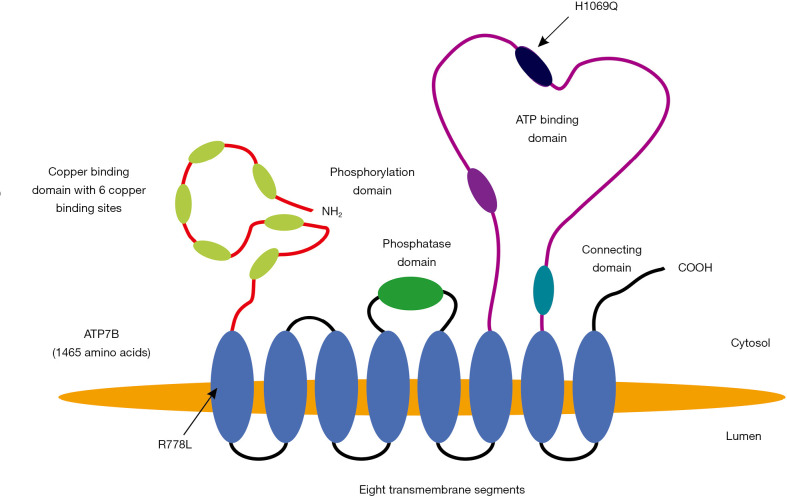
Figure 2.
The conformation of the ATP7B protein and marking of 2 prominent mutations. In humans the mature copper-transporting ATP7B protein consists of 1,465 amino acid encompassing a copper binding domain with six copper binding sites, a phosphatase domain, a phosphorylation domain, an ATP-binding domain, and a short stretch connecting the ATP binding domain to the eight transmembrane segments (2,8). The positions of the two most common mutations R778L (located in the first transmembrane region affecting transport of copper through the membrane) and H1069Q (located in the ATP binding site reducing ATP-mediated phosphorylation) are depicted. However, it is also discussed that mutations induce protein misfolding resulting in endoplasmic-reticulum (ER)-associated degradation (9).