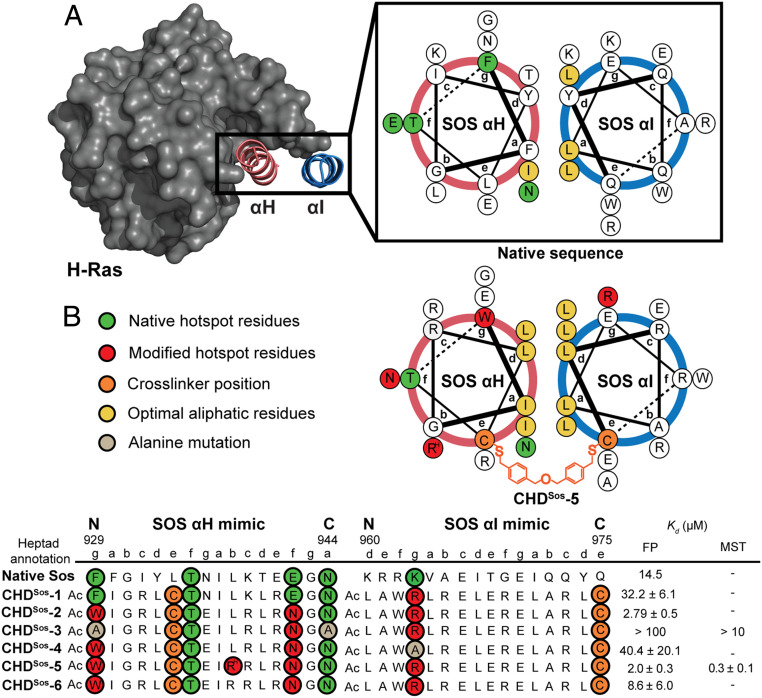
Fig. 2.
Rational design of Sos proteomimetics as Ras ligands. Antiparallel helix wheel diagrams depicting native (Top) Sos helical hairpin and (Bottom) the optimized constrained helix dimer. (A) Sos αH (pink) and αI (blue) helical domains make direct contacts with Sos, with many of the energetically important Ras contacting residues, termed hot-spot residues, positioned on the αH helix. (B) We designed and synthesized constrained Sos mimics with a hydrophobic interface and nonnative residues on both helices to enhance binding interactions with Ras. A dibenzyl ether crosslinker is placed at the “e” position of each helix to enhance conformational stability. The binding affinity of the Sos derivatives for Ras was measured by an FP assay; the binding affinity of the lead derivative CHDSos-5 and alanine control CHDSos-3 was further confirmed by MST. RH, L-homoarginine.