Fig. 3.
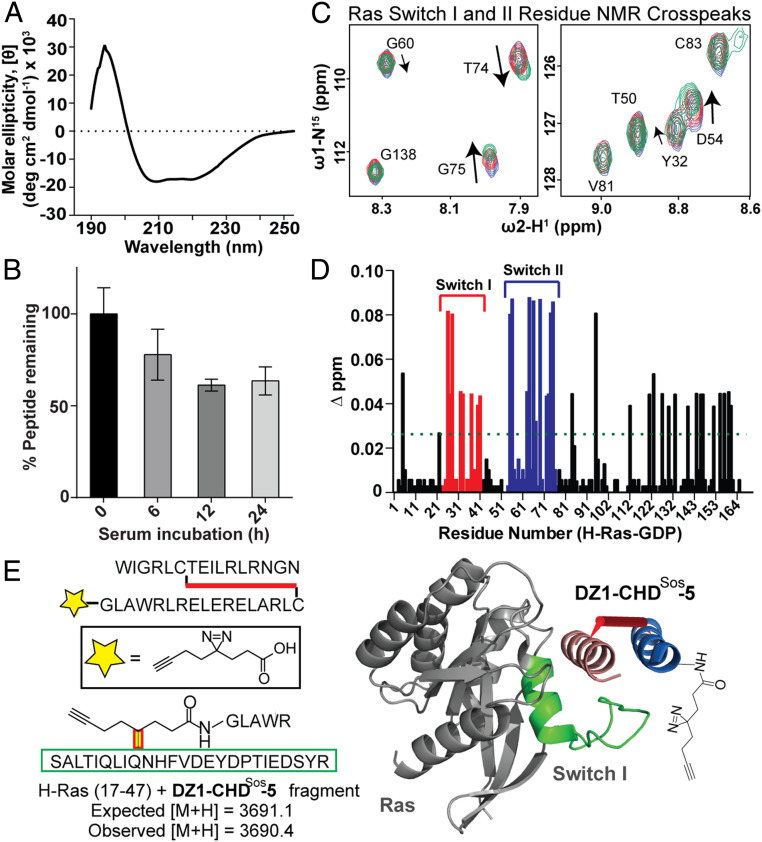
Biophysical characterization, proteolytic stability, and the Ras-binding site analysis of CHDSos-5. (A) CD spectrum of CHDSos-5. The CD study was conducted in 50 mM aqueous potassium fluoride buffer (pH 7.5) at 20 μM peptide concentration. (B) Proteolytic stability of CHDSos-5 in 25% FBS was analyzed in an HPLC assay as discussed in the Materials and Methods. Error bars are mean ± SD of biological replicates. (C) 1H-15N HSQC titration spectra of uniformly 15N-labeled GDP-loaded wild-type H-Ras. Examples of specific Ras residues that shift upon titration with increasing equivalents (1, 2.5, and 5) of CHDSos-5. (D) Bar graph shows mean chemical shift changes observed for the 15N-labeled H-Ras upon titrations with increasing amounts of CHDSos-5. (E) The CHDSos-5 binding site on Ras was further confirmed by a proximity-guided protein crosslinking reaction. DZ1-CHDSos-5 contains a photoactivable diazirine group that reacts with proximal residues on Ras. A fragment with mass corresponding to DZ1-CHDSos-5 crosslinked to Ras Switch I loop was identified. The identified fragment corresponds to the Switch I region and is depicted as a green ribbon in the molecular model.