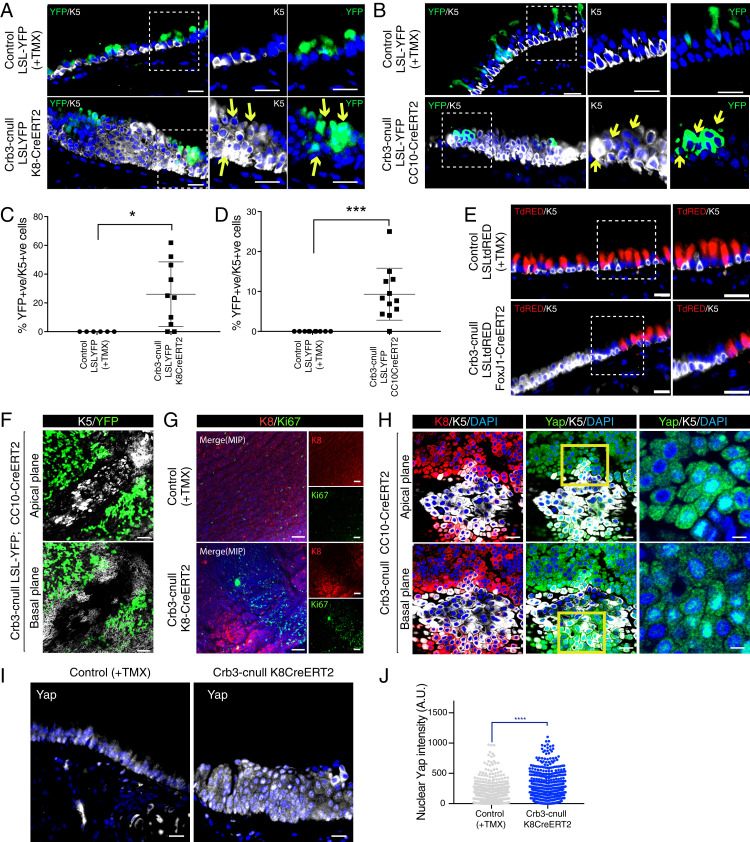
Fig. 2.
Deletion of Crb3 in luminal airway epithelial cells results in luminal-basal plasticity and paracrine cell expansion. (A–D) Conditional deletion of Crb3 using (A) Krt8CreERT2 or (B) CC10CreERT2 in combination with a Lox-STOP-lox-EYFP (LSL-YFP) marker reveals that a population of cells that exhibit Cre activity/YFP expression and expression of the basal cell marker Krt5 (highlighted by the yellow arrows). Images shown are from tissues isolated 21 d post-TMX treatment. (Scale bars, 20 μm.) Quantitation of cells expressing both YFP and Krt5 showed that (C) the Krt8CreERT2 model led to ∼22% of Cre-active/YFP-expressing cells that exhibited basal-like plasticity following Crb3-deletion, and (D) the CC10CreERT2 model led to ∼10% of Cre-active/YFP-expressing cells that exhibited basal-like plasticity following Crb3 deletion. Images from control (n = 10) and the Crb3-cnull tracheas (n = 12 for Krt8CreERT2, and n = 10 for CC10CreERT2) were analyzed by IF for YFP and Krt5 from a minimum of four mice per condition. Shown is the average percentage of Krt5-positive/YFP-positive cells ± SEM. Significance was determined by the use of a Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. ***P < 0.001 and *P < 0.05. (E) Conditional deletion of Crb3 using the FoxJ1CreERT2 model, in combination with a Lox-STOP-lox-TomatoRed (LSL-tdRED) marker, revealed that no Cre-active cells express the basal cell marker Krt5. Images shown are from tissues isolated 21 d post-TMX treatment. (Scale bars, 20 μm.) (F) Whole mount IF imaging of isolated tracheas from YFP lineage–traced Crb3-cnull mice shows that Cre-active/YFP-expressing cells flank luminal expanding Krt5-positive cells. (G and H) Whole mount IF imaging of Crb3-cnull tracheas shows the presence of (G) cells expressing the proliferation maker Ki67, and (H) Krt5 or Krt8/Krt5 double-positive cells (zoomed in image) with high levels of nuclear Yap. Images shown are from tracheas isolated 21 d post-TMX treatment. (Scale bars, 20 μm.) (I) Yap protein was examined by IF microscopy in control and Crb3-cnull trachea tissue sections, revealing elevated nuclear Yap throughout stratified epithelial lesions. (J) Quantitation of nuclear Yap intensity demonstrated significantly higher levels of nuclear Yap in Crb3-cnull trachea epithelium. Shown is the average nuclear Yap intensity ± SEM measured from cells across tracheal tissues isolated from three control and Krt8CreERT2 Crb3-cnull mice 21 d post-TMX treatment. Significance was determined by the use of a Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test for all panels. ****P < 0.0001.