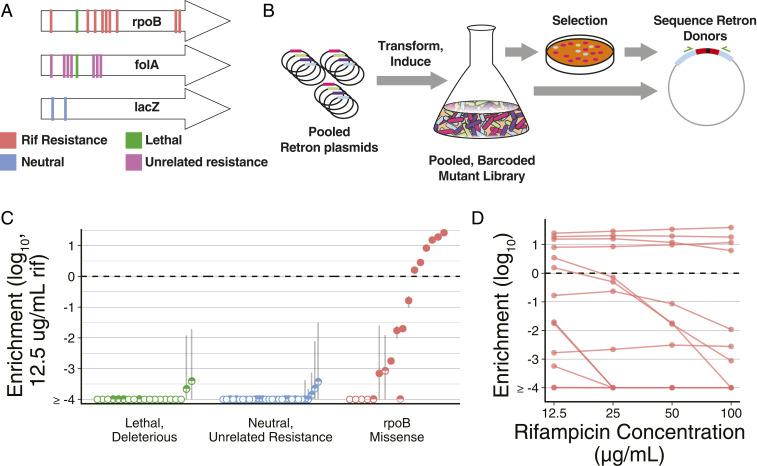
Fig. 3.
Pooled measurement of phenotypes using RLR. (A) The rpoB mutations, including known rifampicin resistance alleles, were specified, as well as resistance alleles for unrelated drugs, and control alleles expected to be neutral, lethal, or deleterious (SI Appendix, Table S3). (B) A pool of Retron plasmids conferring these alleles are transformed into cells. Transformants are induced, and editing produces a pooled, barcoded mutant library. A selection is performed, and frequencies of retron donors are compared before and after treatment for each allele. (C) RLR enrichment values observed with rifampicin treatment. The median of three replicates is indicated with a dot, and error bars are the SE of the mean. Pseudocounts of one are given to alleles not detected after treatment, such that frequencies are a lower limit of detection in these cases. Unfilled points indicate alleles not detected among any replicates after rifampicin treatment, and half-filled points indicate alleles detected in a subset of replicates. An enrichment value of zero is marked with a horizontal dashed line, indicating identical relative abundance before and after selection. (D) For rpoB mutation, allelic enrichment across concentration of rifampicin is displayed. The median of three independent experiments is indicated with a dot, and lines connect an allele across concentrations of rifampicin.