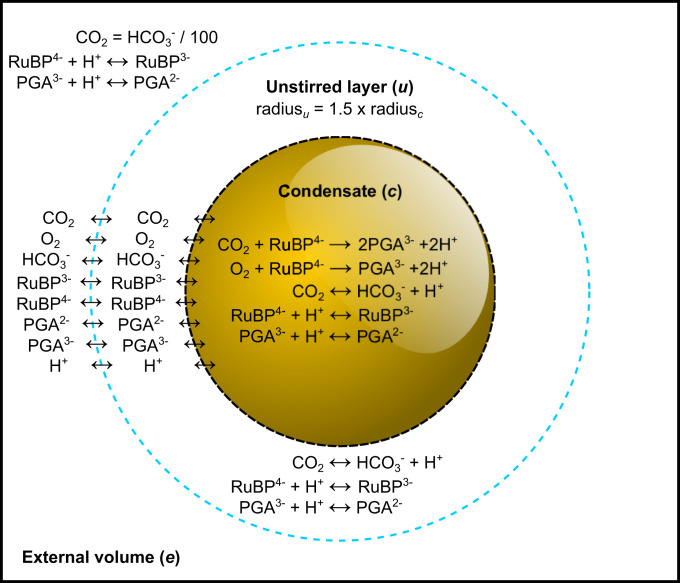
Fig. 1.
Rubisco compartment model. A visual description of the compartment model used in this study. The model consists of three reaction compartments. The external compartment (e) is analogous to a static cellular cytoplasm in which we set the concentration of inorganic carbon (Ci) species (CO2 and HCO3−), along with RuBP and PGA, which can undergo reversible reactions with protons (H+). Interconversion of Ci species in the unstirred (u) and condensate (c) compartments is catalyzed by CA, whereas RuBP and PGA protonation/deprotonation is determined by the rate of conversion at physiological pH given pKa values of relevant functional groups (SI Appendix, Fig. S1). The central compartment of the model is a Rubisco condensate in which Rubisco carboxylation and oxygenation reactions occur, along with RuBP/PGA protonation and CA reactions. In modeling scenarios, we modify external CA by modulating its function in the unstirred layer. The diffusion of all reaction species between each compartment can be set in the model to simulate either a free Rubisco enzyme, a Rubisco condensate, or a carboxysome as described in Table 1. Model parameterization is described in detail in SI Appendix, Methods.