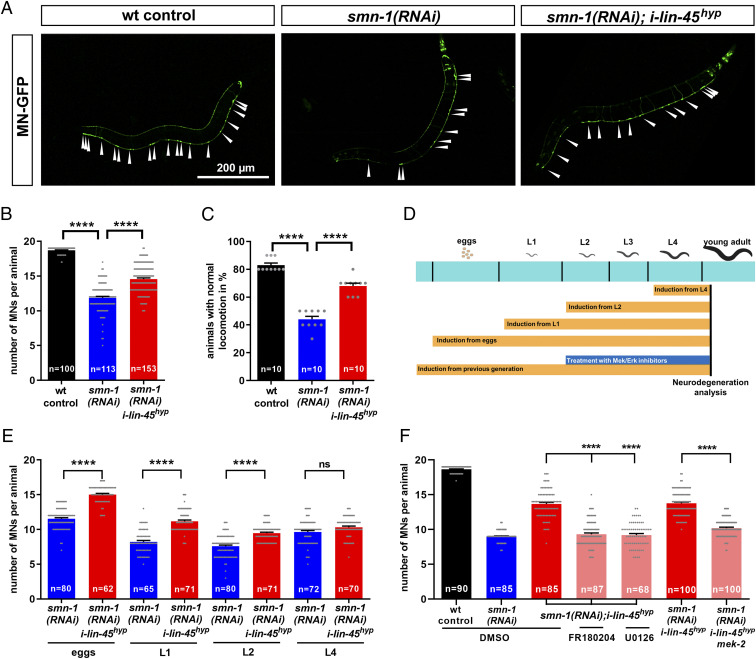
Fig. 5.
The B-Raf homolog lin-45 rescues motoneurons in smn-1–deficient C. elegans via MAPK pathway and after onset of motoneuron degeneration. (A) Representative images of C. elegans animals expressing GFP under the punc-25 promoter, which is exclusively expressed in motoneurons (MN-GFP): arrowheads show individual D-type motoneurons. smn-1 was silenced in D-type motoneurons only [smn-1(RNAi)]. Wild-type animals served as controls (wt control). The temperature-inducible promoter phsp-16 drives the expression of lin-45 hyperactive mutant (i-lin-45hyp). All genotypes were continuously incubated at 25 °C, which induces expression of the lin-45 hyperactive mutant. (B) Motoneurons were identified as distinct GFP-expressing cells and quantified for each animal. (C) The backward locomotion was quantified as the percentage of animals with normal locomotion. (D) Experimental setup of stage-specific temperature induction and lin-45 downstream partner pharmacological inhibition. Strains were grown at 15 °C, and the temperature was increased to 25 °C to induce i-lin-45 expression from different stages: eggs (0 h after eggs were laid), L1 larval stage (∼20 h post eggs laying), L2 larval stage (∼38 h post eggs laying), and L4 larval stage (∼62 h post eggs laying). Motoneuron degeneration was analyzed when animals reached the young adult stage. (E) Motoneurons were identified as distinct GFP expressing cells and quantified in smn-1 silenced animals combined with a temperature-mediated induction of i-lin-45hyp expression from different developmental stages, ranging from eggs to larval stages (eggs, L1, L2, and L4). (F) Motoneurons were identified as distinct GFP-expressing cells and quantified for each animal after treatments of the heat-inducible strain i-lin-45hyp with MEK (U0126, 20 µM) and ERK inhibitors (FR180204, 20 µM) or with a mek-2 mutation. All graphs show individual data points as scatterplots with bars and whiskers displaying mean + SEM. Kruskal–Wallis test was combined with Dunn’s multiple comparison test with ****P ≤ 0.0001 and ns (not significant).