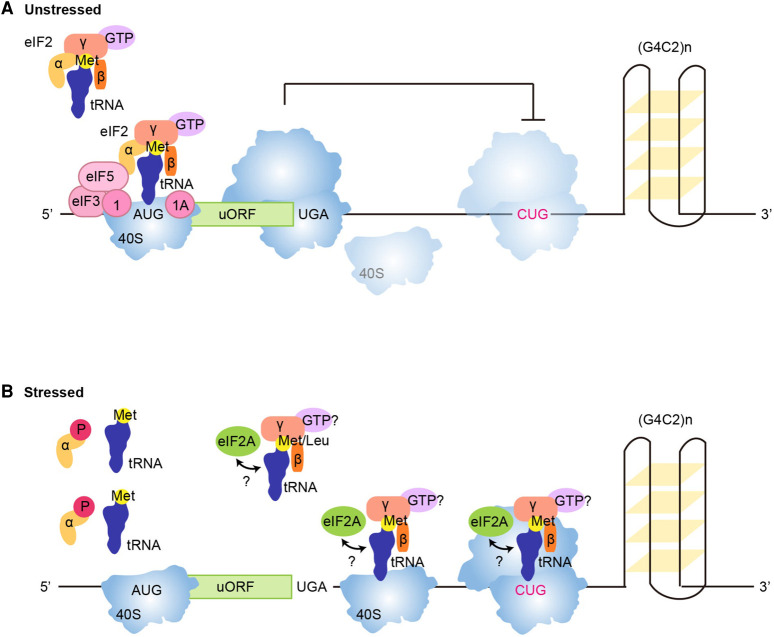
Figure 3. The role of a uORF in the translation of RAN proteins from pathological sense GGGGCC C9ORF72 repeat expansions.
(A) In unstressed cellular conditions, a uORF of 55 nucleotides in length within intron 1 of C9ORF72 inhibits RAN translation of the downstream repeat expansion. The uORF is translated through the canonical translation machinery and ribosomes are unable to reassemble on the mRNA for initiation at the downstream CUG RAN initiation codon. (B) Following cellular stress, phosphorylation of eIF2α prevents its binding of Met-tRNAiMet results in an inhibition of eIF2-driven canonical translation. Consequently, the alternative tRNA recruiting factor eIF2A is able to initiate non-canonical translation. The scanning 40S ribosomal complex scans through the uORF and eIF2A initiates RAN translation at the downstream CUG codon.