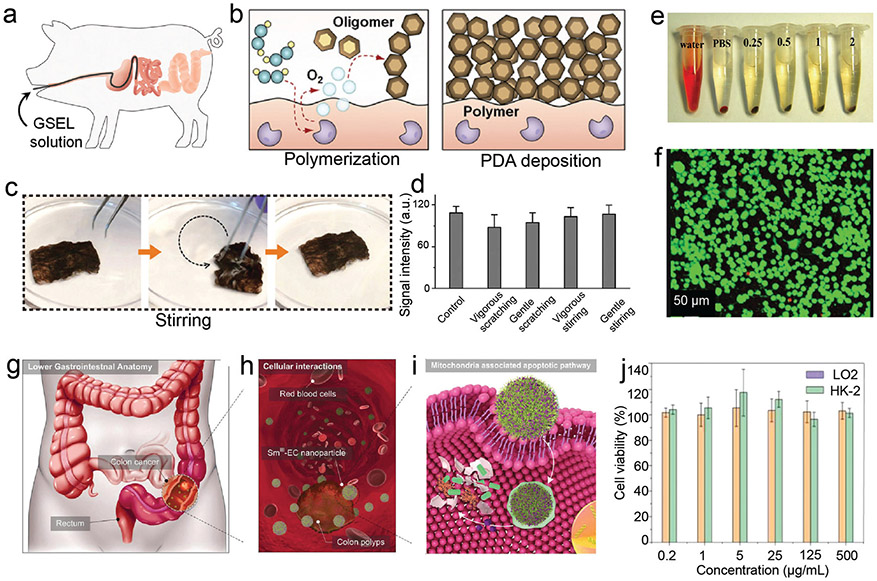
Fig. 19.
Pharmacokinetics and toxicology investigation of phenolic-based materials. (a) Schematic illustration of administration of dopamine solution for gastrointestinal synthetic epithelial lining to porcine small intestine through a catheter. (b) Schematic illustration of enzyme-catalysed polymerization and PDA deposition on epithelium. (c) Representative images of fresh resected tissue specimens from the human small intestine with PDA coating under ex vivo mechanical stirring and scratching. (d) Quantitative ex vivo evaluation of PDA signal intensities of the coated human tissues under a series of physical conditions. (a–d) Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2020, American Association for the Advancement of Science. (e) Hemolysis evaluation of Fe3O4@PDA nanocomposites at varying concentration. (f) Live/dead calcein-AM staining of 4T1 cells treated with Fe3O4@PDA nanocomposites (green: live; orange: dead). (e and f) Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. (g) Overview of the lower gastrointestinal through the endocytosis of Sm(iii)–EC nanoparticles. (h) Cellular interaction between colon polyps and Sm(iii)–EC nanoparticles. (i) Intracellular delivery of functional Sm3+ and EC molecules through the endocytosis of the nanoparticles. (j) Cell viability of normal healthy cells (LO2 and HK-2 cell) treated with Sm(iii)-EC nanoparticles. Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH.