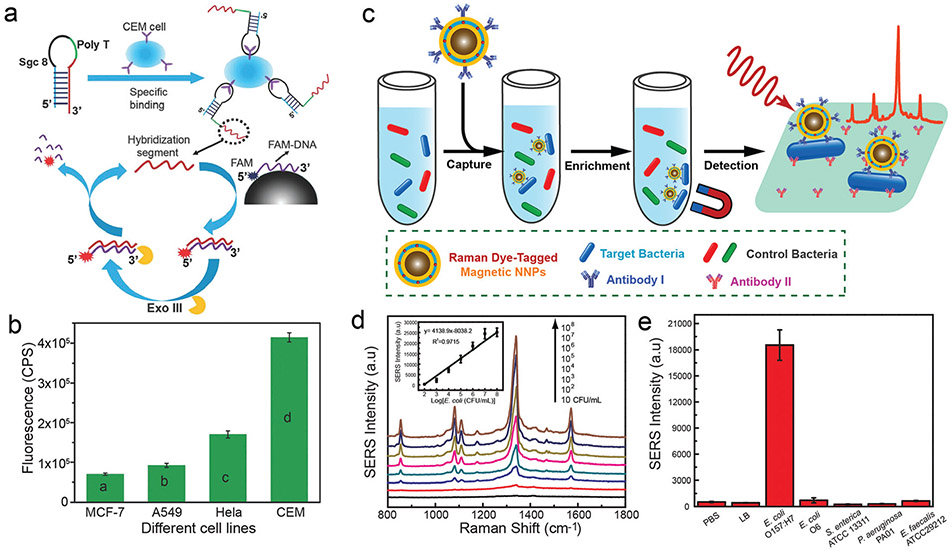
Fig. 22.
In vitro biosensing of diverse cell types via phenolic-based nanoparticles. (a) Proposed mechanism for PDA nanoparticle-based cytosensor for detecting CEM cancer cells. (b) Fluorescence intensity of suspension containing the nanoprobes and different cell lines (e.g., MCF-7, A549, HeLa and CCRF-CEM). (a and b) Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2016, Royal Society of Chemistry. (c) Schematic illustration of the immunoassay using SERS-encoded magnetic nanoprobes for bacterial detection. (d) Raman spectra of E. coli O157:H7 at different concentrations after being conjugated with nanoprobes. Inset: Raman intensity at 1341 cm−1 depends on the logarithm of the bacterial concentration. (e) The detecting selectivity of this platform by using control buffers and various types of bacteria (106 CFU per mL). (c–e) Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society.