FIGURE 1.
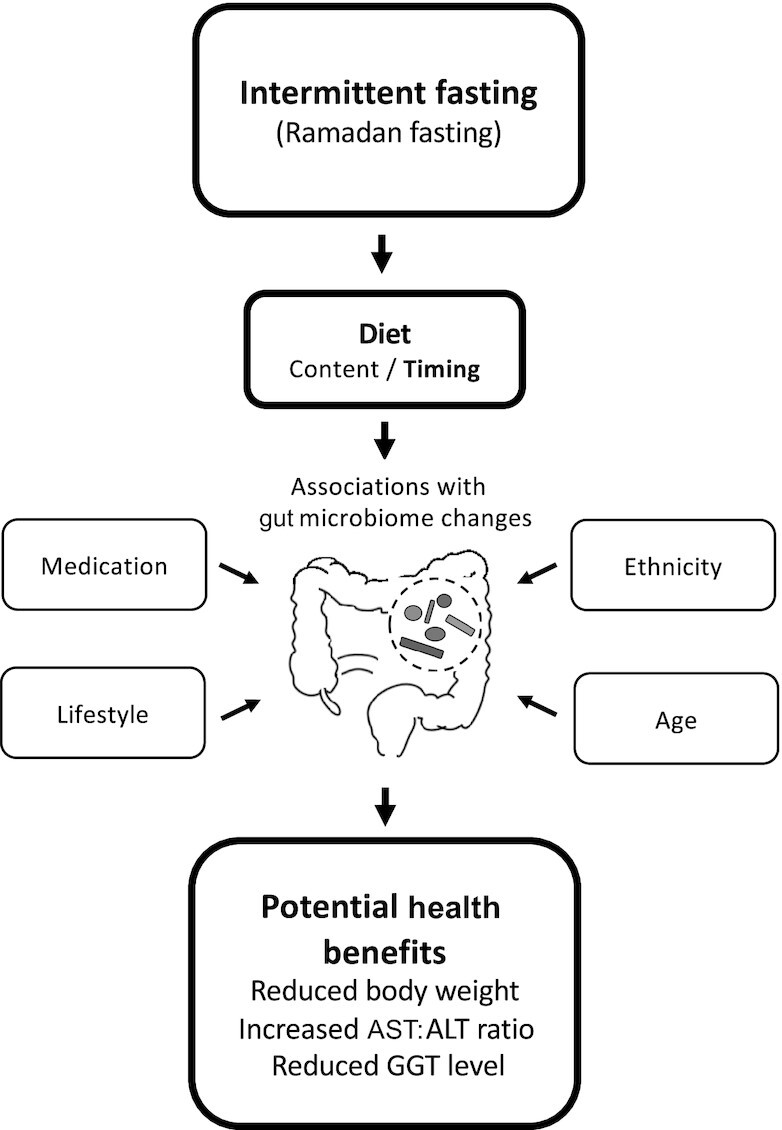
Several factors contribute to potential gut microbiome modulation by intermittent dieting, including diet, ethnicity, age, medication, and lifestyle, affecting human health. Ramadan fasting, a human cultural model of intermittent dietary intervention, is associated with metabolic health benefits and associated microbiome alterations. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; GGT, gamma glutamyl transferase.
