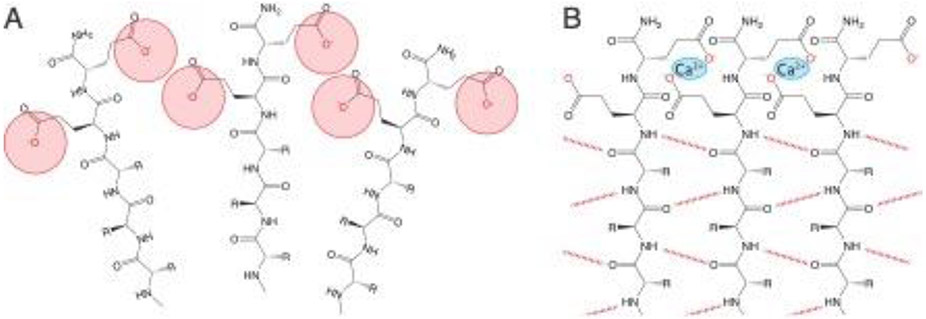
Figure 3:
(A) Self-assembling peptides typically contain hydrophilic domains comprised of charged amino acids, leading to electrostatic repulsion which may disfavor self-assembly under physiological conditions. (B) These repulsive forces can be overcome to drive self-assembly and/or stabilize assembled nanostructures by changing pH or adding ions, like calcium, to screen and/or bridge charged groups.