Figure 1 ∣. Evidence for dopamine as a TD error signal.
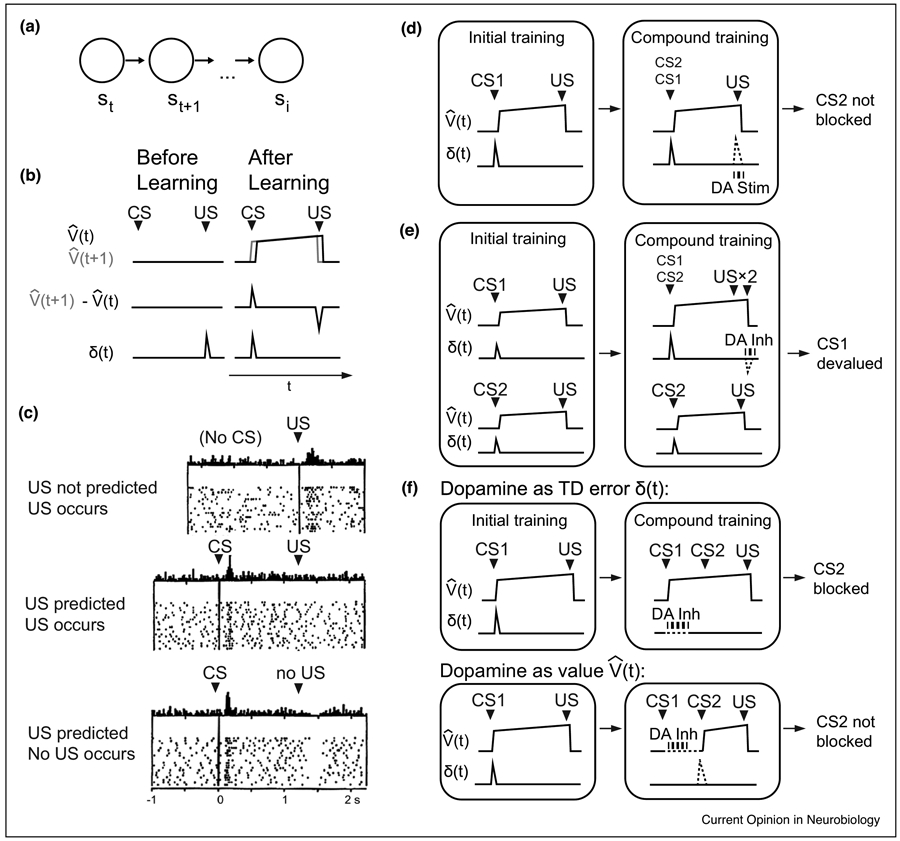
(a) In temporal difference learning, the agent proceeds through ‘states’ s. (b) Value signal, temporal difference of value signal, and error signal δ produced by a simple TD model. (c) Firing pattern of a putative dopaminergic neuron during a classical-conditioning task. From Schultz, Dayan, and Montague 1997 [3]. (d) Dopaminergic stimulation (DA stim) at the time of the US allows a cue that would otherwise be blocked to be learned. This can be modeled as dopaminergic stimulation signaling a positive TD error at the time of the US (dotted line). Based on Steinberg et al, 2013 [5]; Keiflin et al, 2019 [6]. (e) Dopaminergic inhibition (DA inh) at the time of the expected second US in an overexpectation paradigm led to the ‘un-reminded’ CS (CS1) being devalued. This can be modeled as dopaminergic inhibition signaling a negative TD error at the time of the ‘overexpected’ US (dotted line). Based on Chang et al, 2017 [25]. (f) If dopamine signals a TD error, inhibition at the time of a learned CS1 should not affect the value prediction based on CS1, thereby blocking learning of additional value for CS2. If dopamine signals value, dopaminergic inhibition following CS1 should allow learning to occur for CS2 (dotted lines). Experimental results from Maes et al, 2020 [14], supported the hypothesis that dopamine signals a TD error rather than value.
