Figure 3.
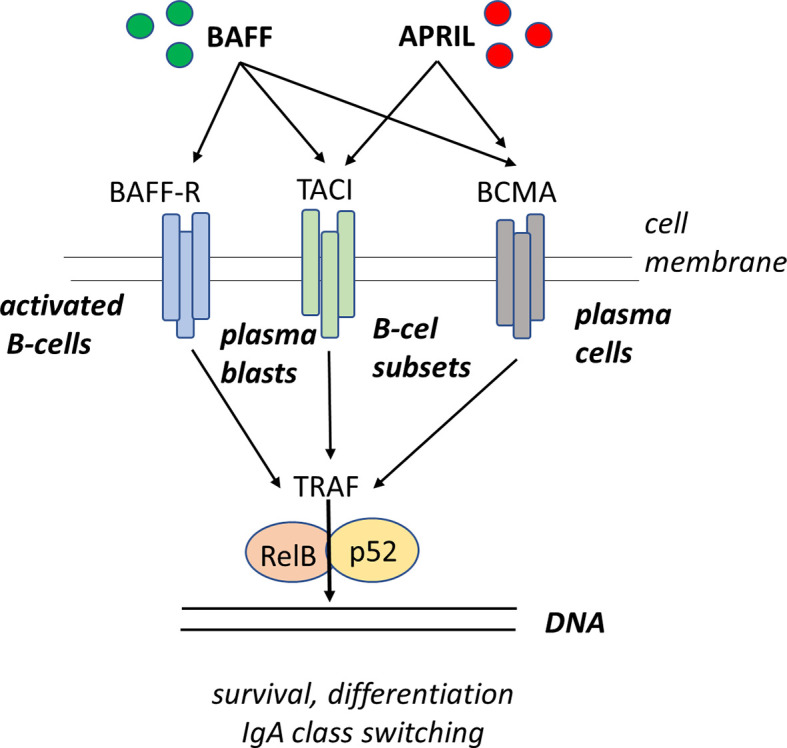
Sequential class switch recombination (CSR) from IgE to IgA2 in activated B-cells. The immunoglobulin heavy chain locus contains a rearranged variable (V) diversity (D) joining (J) exon encoding the antigen-binding domain of the antibody molecule. Upon activation, the B-cell receives specific signal for isotype switching whereby the switch region upstream of the cμ locus (Sμ) integrates with the switch region Sε upstream of the Cε gene segment. As a result, the B-cell produces productive mRNA transcripts that give rise to the formation of IgE molecules. Subsequent exposure to other environmental factors (including TGF-β, APRIL, or BAFF) drives a further CSR event whereby the B-cell fuses the Sε segment to the Sα2 segment, leading to a productive switching to IgA2. As the switching process occurs from 5’ to 3’ and all isotype gene segments that are skipped will be deleted upon the next cell division an IgE-secreting B-cell has only one option left for subsequent CSR which is to move to IgA2.
