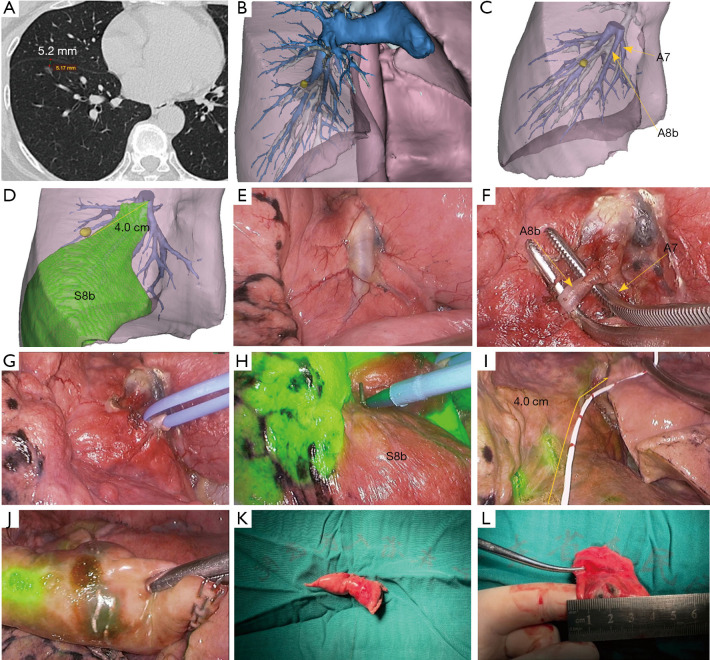
Figure 2.
Localizing the nodule on the boundary of negative staining using watershed analysis. (A) Preoperative computed tomography scan shows a pure ground-glass nodule that appeared in the anterior basal segment of the right lower lobe with the depth of 5.2 mm from the pleura; (B,C) three-dimensional reconstruction model of the lesion and anatomy of the target subsegmental artery; (D) the lesion was located on the negative staining boundary of the target area with a distance of about 4 cm from the bifurcation of A8b and A7; (E,F) identifying the target artery intraoperatively; (G) the colored ribbon was used to ligate the target subsegmental artery with a slipknot; (H) Observation of the lung using an infrared thoracoscopy system after an intravenous injection of indocyanine green (2.5 mg/mL) and marking of the white-to-blue transitional zone by electrocautery; (I) the 4-cm measuring tube was used to determine the exact location of the nodule on the negative staining boundary; (J,K,L) wedge resection was performed, and the lesion was confirmed.