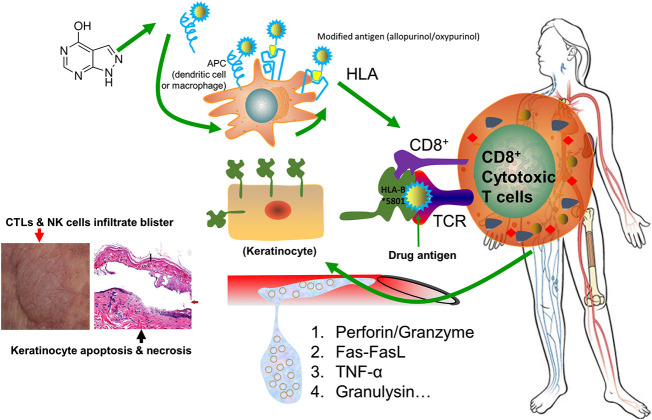
FIGURE 2.
Schematic representation of immunopathogenic mechanism underlying drug-induced SJS/TEN. The drug allopurinol is listed as the demonstrating drug. Allopurinol and/or its active metabolite oxypurinol is presented by antigen presenting cells (APC) and is interacting with HLA-B*58:01 protein. They are capable of generating a sufficient strong signal to TCR for cell activation. Upon activation, the stimulated CD8+ cytotoxic T cells will have a cascade release of cytokines or chemokines, including perforin/granzyme, Fas-FasL, TNF-α, and granulysin, which will kill keratinocytes and mucosal cells causing skin sloughing and necrosis. Meanwhile, CTLs and NK cells will infiltrate into the skin to form blisters. The left bottom image illustrates keratinocyte necrosis (black arrow) and development of large bullae (red arrow), adapted from (Gupta et al., 2019). Abbreviations: APC: antigen presenting cells. APCs include dendritic cells, macrophages, Langerhans cells, and B cells. TCR: T-cell receptor. CTLs: cytotoxic T lymphocytes. NK cells: natural killer cells.