Figure 1.
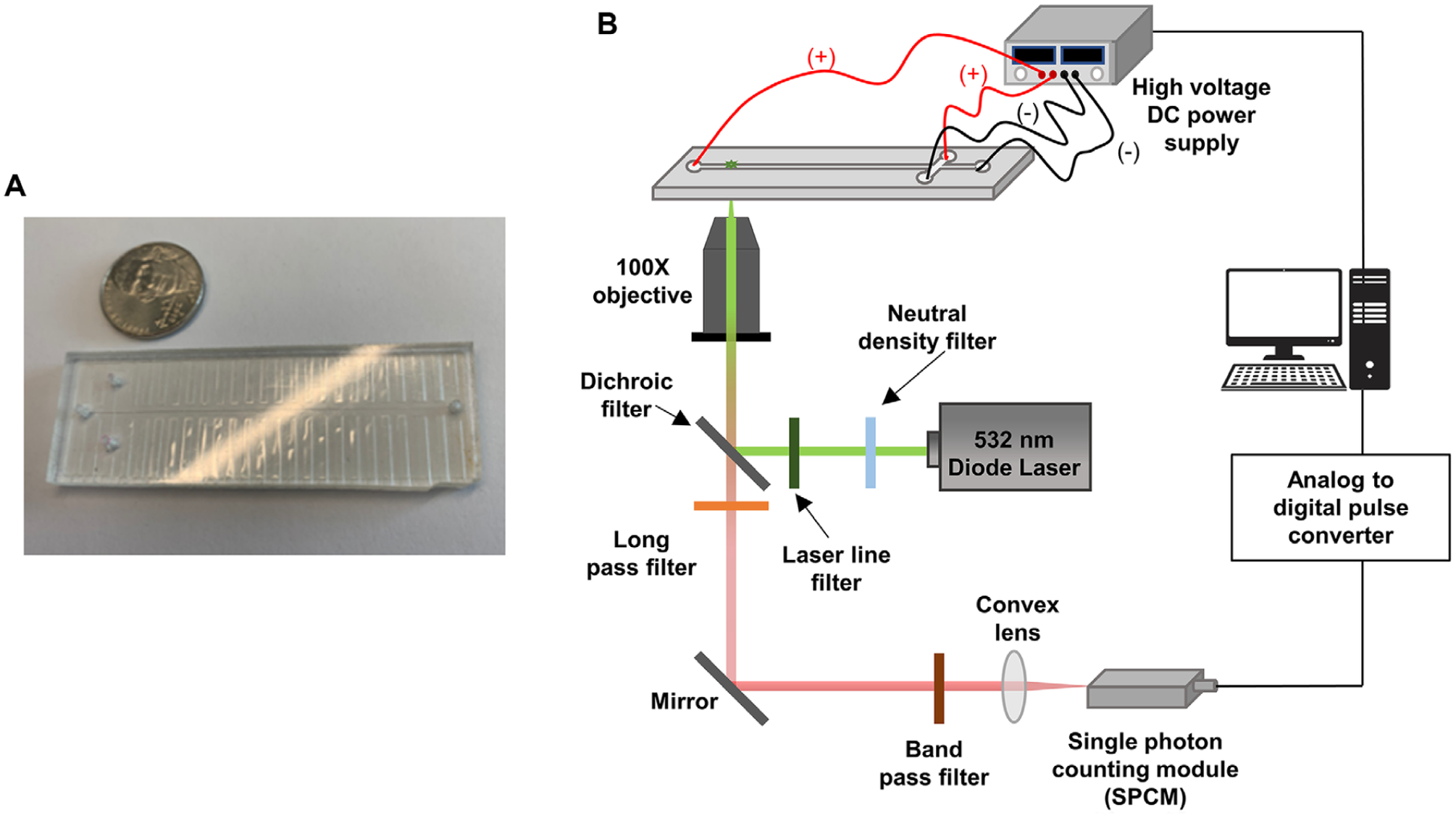
(A) An image of the T-chip used for the microscale electrophoresis. The chip was made via hot embossing into PMMA. (B) Schematic diagram of the in-house built microchip electrophoresis laser-induced fluorescence detector that utilized a 20 mW, 532 nm excitation laser with edge filter. The detector contained a 560 nm long pass filter, 532 nm dichroic filter and SPCM-AQR single photon counting module within the optical train. A 100× high numerical aperture (NA = 1.3) microscope objective was used to focus the laser beam onto the microchannel and collect the fluorescence.
