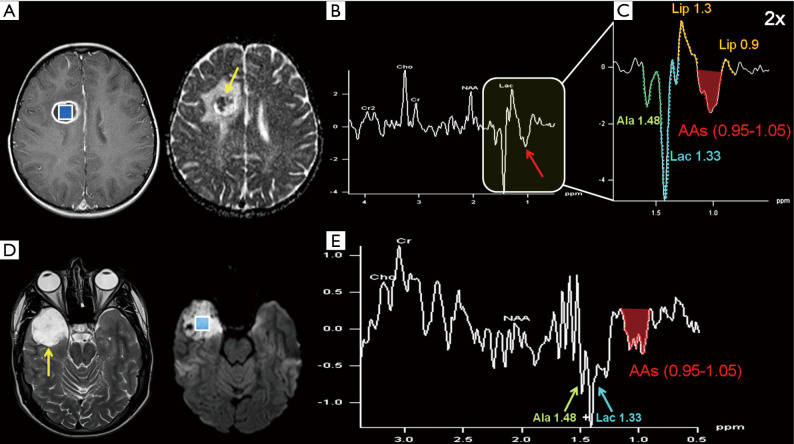
Figure 11.
Top row. A 4-year-old female suffering from sudden headache, nausea and a first epileptic seizure: (A) axial post-gadolinium T1-WI shows the selected H1MRS voxel (2D-CSI; TE 135 ms; 1.5 cm3 nominal size) chosen inside a well-defined hypointense lesion with ring enhancement in the right frontal lobe; DWI (yellow arrow in ADC map in A) shows inhomogeneous signal with both restricted and increased diffusion within the lesion. Despite some contamination from normal brain tissue, the spectrum clearly depicts the resonances of Ala + Lac (1.48 & 1.33 ppm), Lip (1.3 & 0.9 ppm), and cytosolic amino acids (AAs, 0.95–1.05 ppm, red arrow in B and red area in 2× magnified spectrum in C). The resonances from Ala, Lac, and AAs are inverted at this intermediate TE value, owing to J-modulation. Ala and Lac resonances are partially fused (a prominent “sum peak” is centered at ~1.4 ppm). A pyogenic abscess (Streptococcus viridans) was confirmed after stereotactic drainage. Bottom row: right temporo-polar epidermoid cyst (T2-hyperintense signal, restricted diffusion and SVS VOI placement fully inside the lesion are depicted in D) in a male patient which became symptomatic at the age of 20 (headache and a first epileptic seizure). The 135 ms TE spectrum (E) demonstrated a complex “sum peak” similar to the one in (B), within the 0.9–1.5 ppm frequency range, but without significant Lip contribution. An inflammatory reaction in the context of the epidermoid cyst, maybe responsible for the onset of symptoms, was neuropathologically proven after resection of the lesion. Acronyms and abbreviations are shown in Appendix 1.