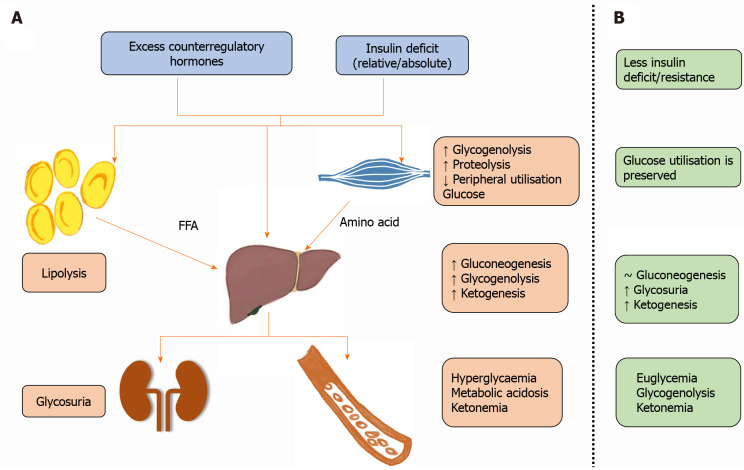
Figure 1.
Ketone bodies (beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone) are responsible for metabolic acidosis, while hyperglycemia through glycosuria and osmotic diuresis causes dehydration and hypovolemia. A: Pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis; B: Pathophysiology of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. FFA: Free fatty acids; ↑: Increase; ↓: Decrease; ~: No change.