Fig. 1. Sequence and structure of human acid-β-glucosidase.
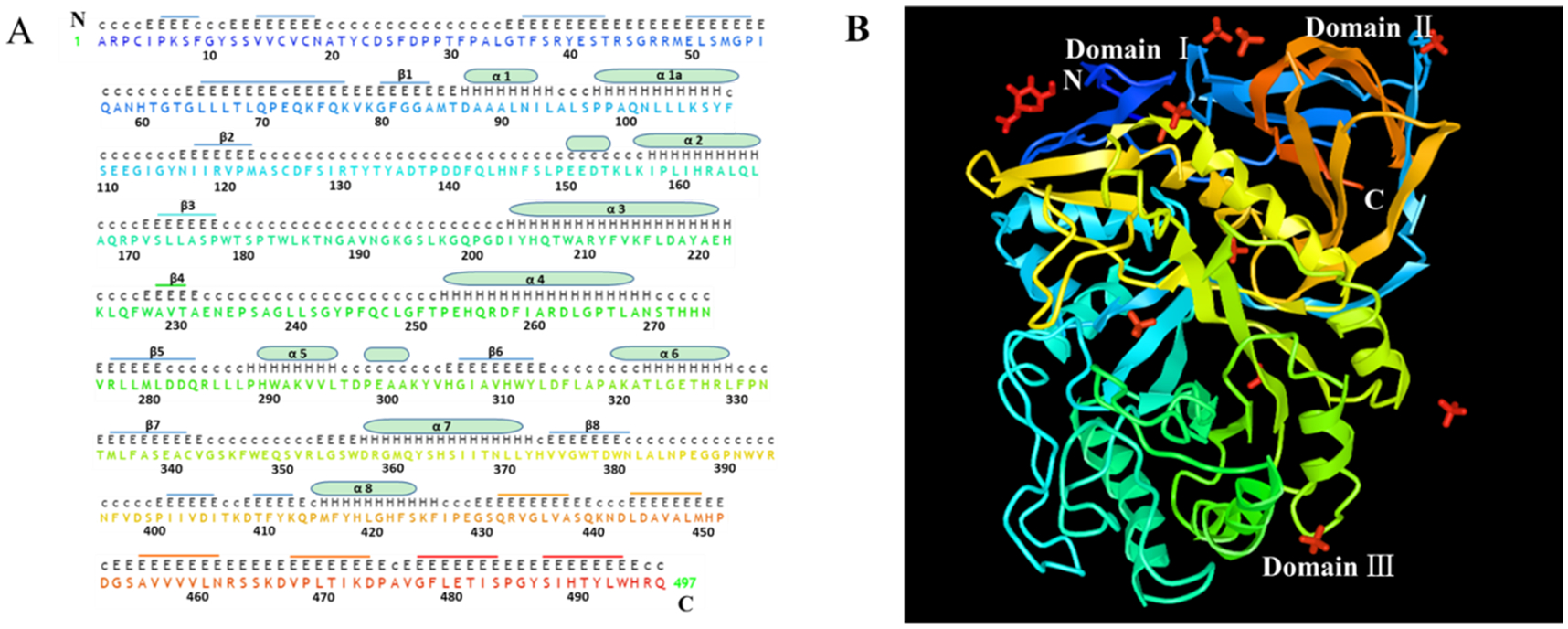
A. The sequence of human acid-β-glucosidase has a total of 497 amino acid residues in which there are eight α helices displayed with cylinders and eight β-strands indicated by stubs. The sequences and stubs in discrepant colors are correspondently presented in X-ray structure in panel B. The upper upper-case letters are the nonstandard residues with coordinates and the upper lower-case letters are the nonstandard residues missing coordinates. The lower upper-case letters indicate the standard residues and the numbers are for amino acid sequence location. B. X-ray structure of α helices and β-strands of human acid-β-glucosidase (from NCBI structure database PDB ID 10GS viewed by iCn3D, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/icn3d/full.html?showseq=1&mmdbid=23543&buidx=1). Acid-β-glucosidase has one N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (top left corner in red color), ten sulfate ions (four limbs in red color), and three domains: domain Ⅰ(aa1-aa29 and aa384–414), domain Ⅱ (an immunoglobulin-like domain consists of aa30-aa76 and aa429-aa497) and domain Ⅲ (a catalytic domain, which is a TIM barrel and contains aa77-aa383 and aa415-aa428).
