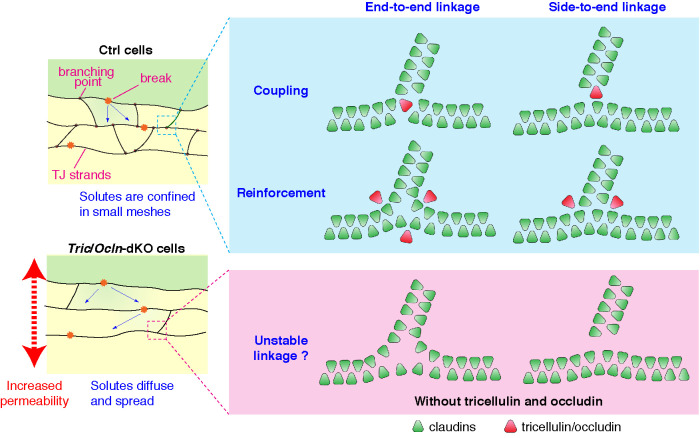
FIGURE 7:
Hypothetical working models for how tricellulin and occludin contribute to the TJ assembly and barrier function. Schematic diagram of branching points of claudin-based TJ strands in the presence or absence of tricellulin/occludin expression. TJ strands are connected to each other in either end-to-end (left) or end-to-side (right) manner at the branching points. Tricellulin and occludin may facilitate the formation of branching points by directly connecting strands (coupling model) or stabilizing the linkage of junctions (reinforcement model). In the Ctrl cells, the solutes entering the strand network through breaks are confined in the compartment. On the other hand, in the absence of tricellulin/occludin, the solutes easily diffuse and spread to interstrand spaces, which results in an increased permeability.