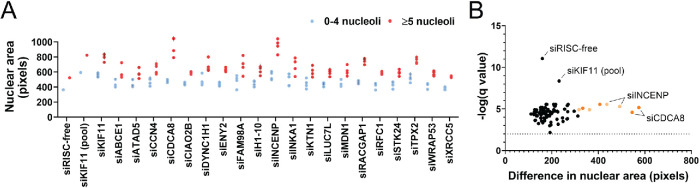
FIGURE 4:
Nuclear area is significantly greater in nuclei with ≥5 nucleoli. (A) Nuclear area is greater in nuclei with ≥5 nucleoli, including in the siRISC-free treatment. Nuclear area was quantified in pixels using analysis of the Hoechst-stained images collected for screen validation by oligonucleotide deconvolution. Three replicates were analyzed for each screen hit depletion, and six replicates were analyzed in this analysis for the controls, siRISC-free and siKIF11 (pool). Blue dots = nuclei with 0–4 nucleoli. Red dots = nuclei with ≥5 nucleoli. Each dot represents the mean ± SD of an individual siRNA (SD = black vertical line). For each blue dot there is a corresponding red dot (Supplemental Table S3). (B) Volcano plot of the statistical analysis of the data in A reveals that in all depletion conditions, including siRISC-free, nuclei with ≥5 nucleoli are significantly larger that nuclei with 0–4 nucleoli. Unpaired t tests were performed, and significance was determined based on a false discovery rate approach using the two-stage step-up method of Benjamini et al. (2006) (n = 3 or 6; q < 0.01/-log q-value > 2; Supplemental Table S3). The x-axis represents the difference in nuclear area between nuclei with 0–4 nucleoli and ≥5 nucleoli. The purple dots = individual siRNAs with the greatest difference between the two categories. Light orange dots = siINCENP individual siRNAs. Dark orange dots = siCDCA8 individual siRNAs.