Figure 5.
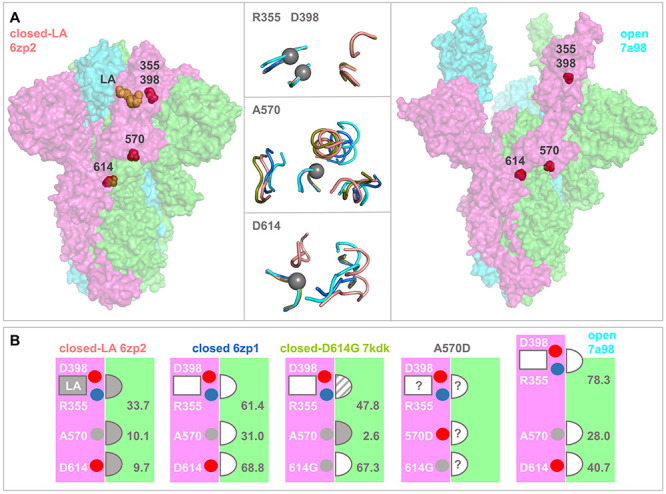
Structural comparisons of monomer—monomer interfacial regions in S protein trimers. (A) Spike protein ectodomain trimers are drawn in surface representation for a closed LA-bound structure (left, 6zp2), and a fully open trimer extracted from a complex with three receptors (right, chains A, B, C from 7a98). Sites of current interest within these transparent surfaces are indicated by red spheres, and LA is drawn in orange. In the horizontal centre are tube cartoon representations of 6zp2 and 7a98, alongside 6zp1 (closed, no LA) and 7kdk (closed, D614G), drawn for regions within 10 Å of R355 (upper), A570 (centre) and D614 (lower). Centres are shown with grey spheres on the Cα atoms of D398/R355, A570, or D614, and other than the regions containing these residues, all other segments are from a neighbouring monomer. The cartoons are colour-coded according to structure, 6zp2/orange, 6zp1/marine, 7kdk/olive, 7a98/cyan. Separate structural alignments were made for each panel, aligning the peptides containing R355, A570, or D/G614 to that of 6zp2. (B) Structure colour-coding is reproduced in the titles of these schematic plots. Each schematic represents the accessibility of each of the R355, A570, D614 residues at the interface between neighbouring monomers (pink and green). LA is bound only to 6zp2, with the most close-packed interface as determined from panel A, and also from the listed solvent accessibility values (Å2). The semi-circular sites are indicated throughout as closely packed (filled in), not closely packed (unfilled), or intermediate (dashed). In the absence of a known structure for interfacial regions in an S trimer bearing the A570D mutation, the degree of packing at monomer—monomer sites is unknown, as shown. In the schematic images, residues of interest are indicated as small spheres, red/acidic, blue/basic, grey/aliphatic.
