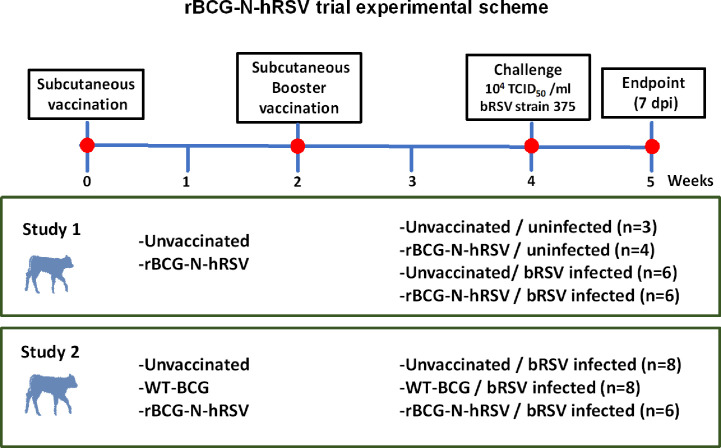
Figure 1.
Diagram for the experimental design for studies 1 and 2. Newborn Holstein calves were vaccinated subcutaneously with GMP rBCG-N-hRSV (Studies 1 and 2) or WT BCG (Study 2) and boosted 14 days after prime immunization. Control calves were left unimmunized. After each immunization, animals were monitored for systemic alterations or local reactions to vaccination. Throughout the study, blood was collected weekly from the jugular vein. Fourteen days after the booster, calves were infected with bRSV strain 375 via aerosol inoculation. For Study 1, groups were: unimmunized, uninfected (n=3); rBCG-N-hRSV, uninfected (n=4); unvaccinated, bRSV infected (n=6); and rBCG-N-hRSV vaccinated, bRSV infected (n=6). For Study 2, groups were: Unvaccinated (n=8), WT-BCG vaccinated (n=8), and rBCG-N-hRSV vaccinated (n=6), being all animals bRSV-infected Animals were monitored and sampled daily after challenge to obtain blood and nasal fluid samples. All animals were euthanized 7 dpi for pathological evaluation and sampling.