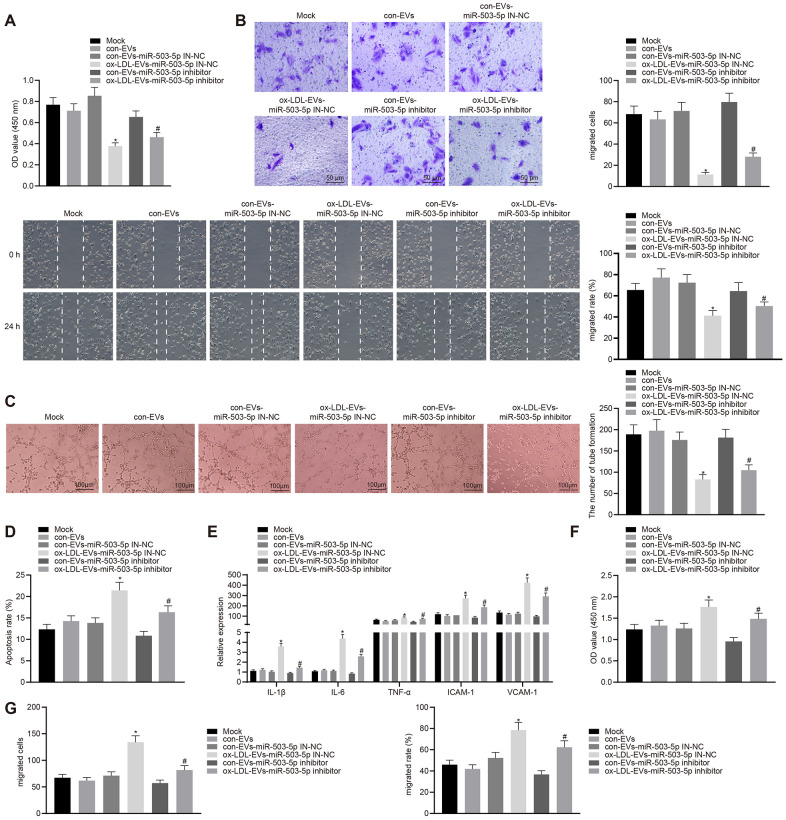
Figure 6.
Macrophage-EVs carrying miR-503-5p inhibit proliferation, migration, and angiogenic abilities of HCAECs while promoting proliferation and migration of HCASMCs. HCAECs and HCASMCs treated with miR-503-5p inhibitor (with miR-503-5p in-NC as control) were co-cultured with EVs released by RAW264.7 cells with or without ox-LDL treatment. (A) Proliferation of HCAECs detected by CCK-8 assay. (B) Migration of HCAECs detected by transwell migration assays and scratch test. (C) Vessel like tubes formed in HCAECs detected by Matrigel-based angiogenesis assays; Scale bar = 20 μm. (D) Apoptosis of HCAECs detected by flow cytometry. (E) Expression of pro-inflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) and adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) measured by ELISA methods. (F) Proliferation of HCASMCs detected by CCK-8 assay. (G) Migration of HCASMCs detected by transwell migration assays and scratch test. Values obtained from three independent experiments in triplicate were analyzed b y oneway ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test among three or more groups. *p < 0.05 compared with miR-inhibitor NC-treated HCAECs co-cultured with EVs in the absence of ox-LDL; # p < 0.05 compared with miR-503-5p inhibitor-treated HCAECs co-cultured with EVs in the absence of ox-LDL.