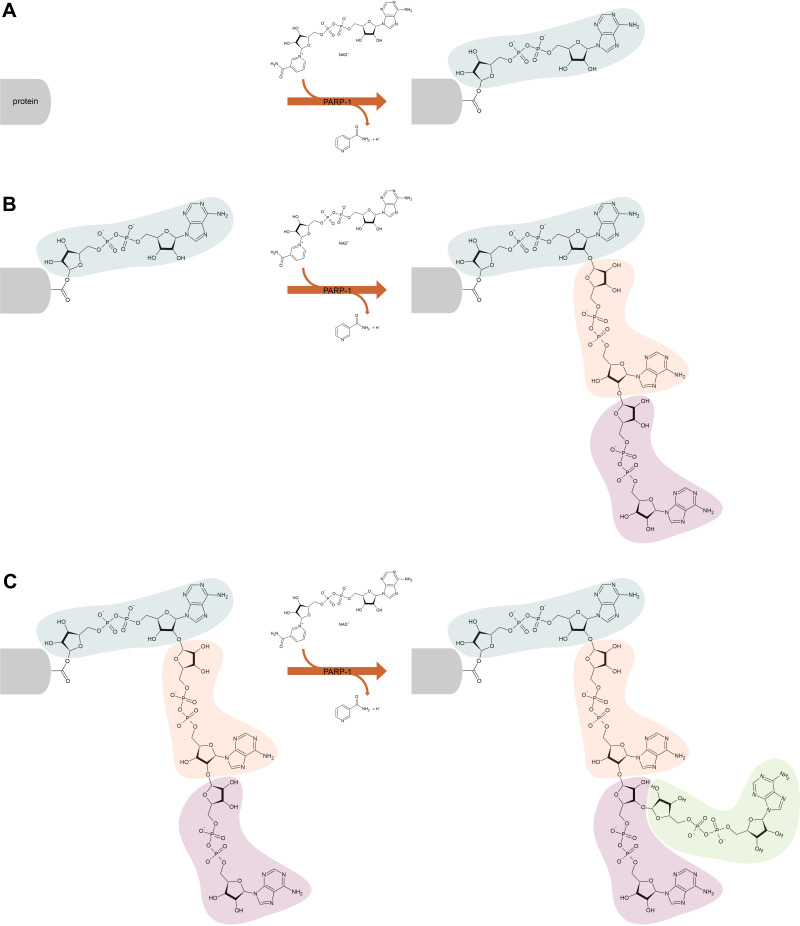
Figure 1.
Scheme of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) catalyzed poly (ADP-ribosylation) of the target protein. The PARP-1 catalytic domain attaches ADP-ribose polymers to proteins, catalyzing three different reactions – initiation (A), elongation (B) and branching (C). Initiation is the attachment of the first ADP-ribose monomer to the amino acid residue of the acceptor protein. Elongation, the attachment of further monomers, takes place through the formation of a (2ʹ-1ʹʹ) ribose-ribose glycosidic bond. Branching involves the creation of a ribose-ribose bond between ADP-ribose (2ʹʹ-1ʹʹʹ) units.