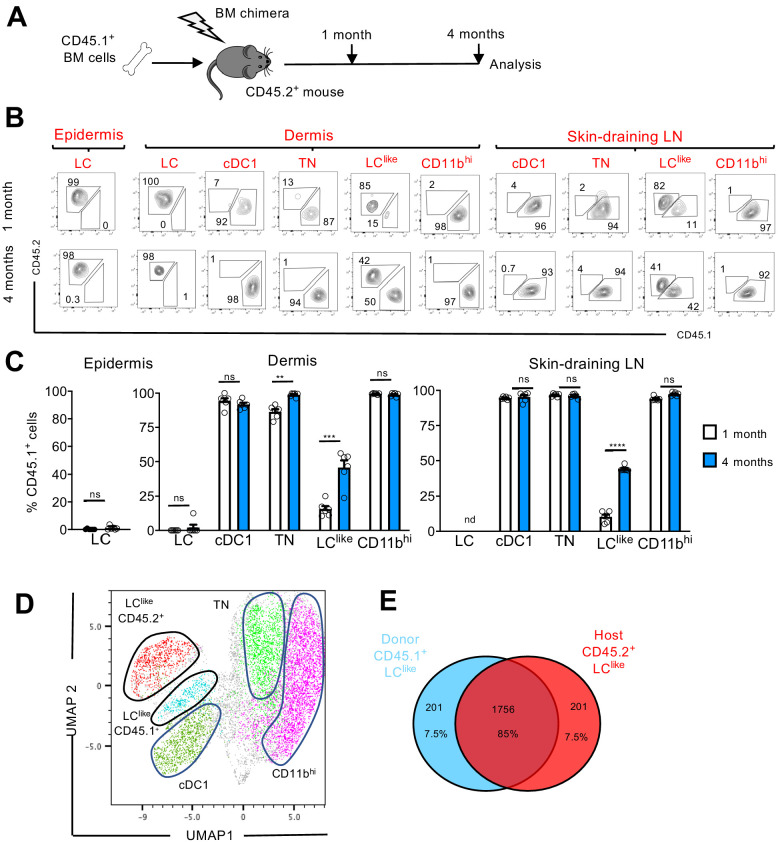
Figure 5. LClike cells derived from embryonic and adult haematopoiesis have a similar transcriptomic signature.
(A) Generation of BM chimeras: CD45.1+ WT BM cells (106) were transferred into lethally irradiated CD45.2+ recipient mice. The epidermis, dermis, and draining lymph nodes (LNs) obtained from the reconstituted chimeras were analysed 1 and 4 months later by flow cytometry. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of donor (CD45.1+) and host (CD45.2+) chimerism in different epidermal, dermal, and skin-draining LN LC and dendritic cell (DC) subpopulations, 1 and 4 months after reconstitution. LC, cDC1, triple negative (TN), LClike, and CD11bhi subsets were gated and analysed for CD45.1 (x-axis) and CD45.2 (y-axis) expression. (C) The percentage of CD45.1 donor cells detected in the epidermis, dermis, and skin-draining LNs of chimeras, 1 or 4 months after reconstitution. Data are represented as mean ± SEM; n = 6 single mice; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001; ns, non-significant; two-tailed Student’s t-test. (D) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) analysis of distinct LN DC subpopulations obtained from chimeras 4 months after reconstitution, based on the expression of different markers (CD11c, MHCII, CD103, CD11b, CD326, CD207, CD45.1, CD45.2). (E) Transcriptome analysis of LN CD45.1+ LClike cells (n = 3) and LN CD45.2+ LClike (n = 3) cells collected from 10 mice. The Venn diagram shows the percentage of overlapping genes expressed by CD45.1+ and CD45.2+ LClike cells.