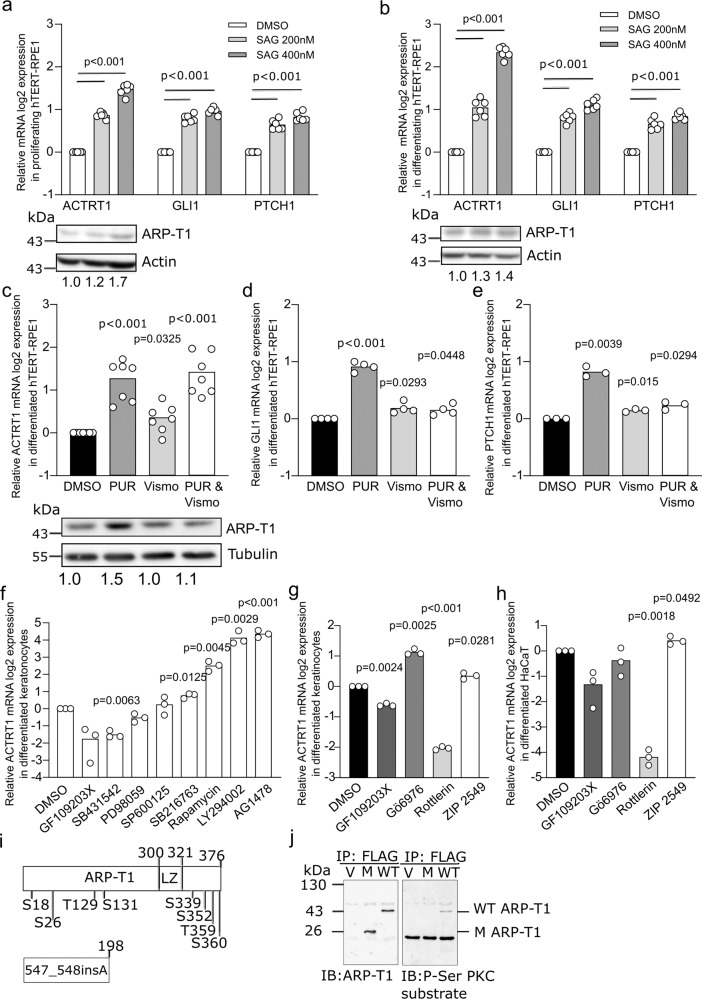
Fig. 2. ACTRT1 is regulated by non-canonical Hedgehog signaling pathway and by protein kinase C delta.
a, b Relative ACTRT1, GLI1, and PTCH1 mRNA expression (a, b N = 6) and ARP-T1 expression (a N = 4; b N = 3) upon treatment with SAG in hTERT-RPE1 cells under proliferative (a) and differentiating (b) conditions. Actin is used as loading control for ARP-T1 expression. Numbers under the blots present the fold change expression of ARP-T1 compared to the vehicle (DMSO) treatment. c–e Relative ACTRT1 (c N = 7), GLI1 (d N = 4), PTCH1 (e N = 3) mRNA expression and ARP-T1 expression (c N = 4) upon treatment with purmorphamine (PUR) and/or vismodegib (VISMO) in differentiated hTERT-RPE1 cells. Tubulin is used as loading control for ARP-T1 expression. Numbers beneath the blots represent the fold change expression of ARP-T1 compared to the vehicle treatment. f, g Relative ACTRT1 mRNA expression upon treatment with different protein kinase inhibitors (f) or with PKC inhibitors (g) in differentiated NHEK (N = 3). h Relative ACTRT1 mRNA expression upon treatment with PKC inhibitors in differentiated HaCaT cells (N = 3). a–h Data are presented as means of the fold change compared to the value of vehicle-treated samples. Each open circle represents one independent experiment. i Schematic representation of ARP-T1 and ARP-T1 mutant (547_548insA) with predicted phosphorylation sites. j ARP-T1 and Phospho-Serine (P-Ser) PKC expression in NHEK transduced with lentiviral vectors, empty vector (V), ACTRT1 mutant (M), and ACTRT1 WT (WT), after immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody M2-conjugated agarose.