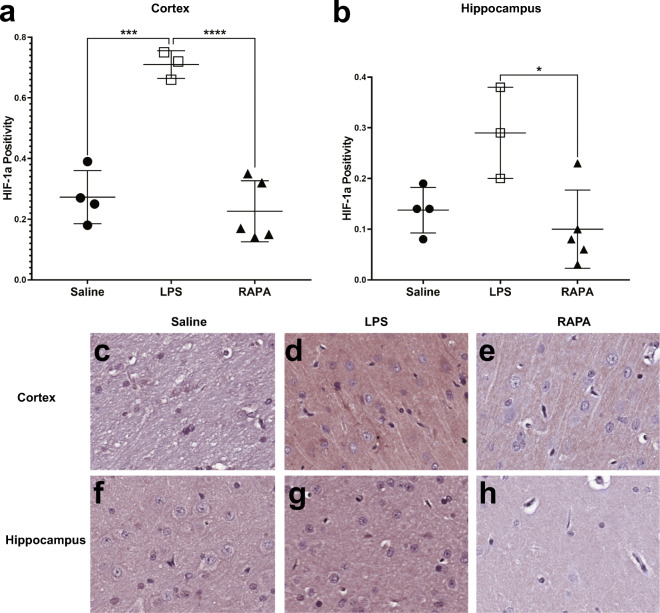
Fig. 6.
Rapamycin restores inflammatory signaling molecule, HIF-1α, levels to normal in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus regions. Quantitative assessment of positivity staining for HIF-1α in the cortex (A) or hippocampus (B) regions of rat brains treated with either saline (n = 4), LPS (n = 3), or LPS + RAPA (n = 5). There was a significant increase in HIF-1α levels in LPS-treated rat brains compared to saline controls, and a significant decrease in HIF-1α levels in the LPS + RAPA-treated rat brains, compared to LPS-alone. Statistical analyses were performed using ANOVA with multiple comparisons. IHC staining for HIF-1α is shown in representative tissue slices in either the cortex (middle panel) or hippocampus (lower panel) regions for saline- (C or F, respectively), LPS- (D or G, respectively), or LPS + RAPA- (E or H, respectively) treated rat brains at 6 weeks post-LPS