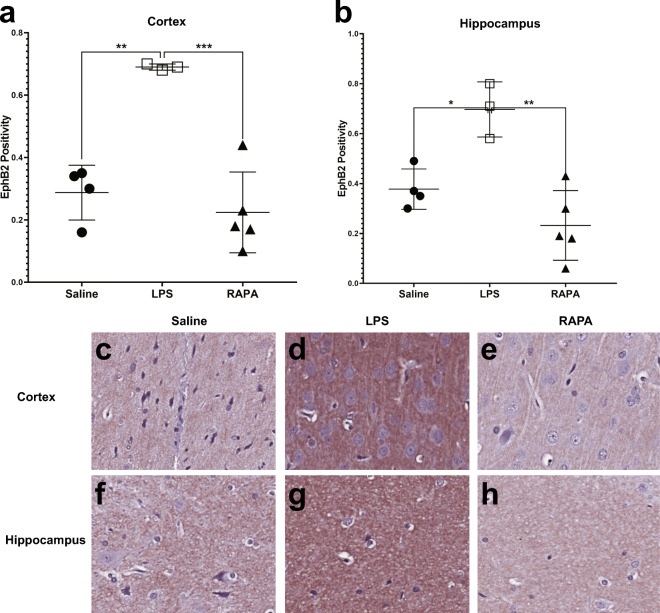
Fig. 7.
Rapamycin restores neuronal Ephrin receptor, EphB2, levels to normal in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus regions. Quantitative assessment of positivity staining for EphB2 in the cortex (A) or hippocampus (B) regions of rat brains treated with either saline (n = 4), LPS (n = 3), or LPS + RAPA (n = 5). There was a significant increase in EphB2 levels in LPS-treated rat brains, compared to saline controls, and a significant decrease in EphB2 levels in the LPS + RAPA-treated rat brains compared to LPS-alone. Statistical analyses were performed using ANOVA with multiple comparisons. IHC staining for EphB2 is shown in representative tissue slices in either the cortex (middle panel) or hippocampus (lower panel) regions for saline- (C or F, respectively), LPS- (D or G, respectively), or LPS+RAPA- (E or H, respectively) treated rat brains at 6 weeks post-LPS