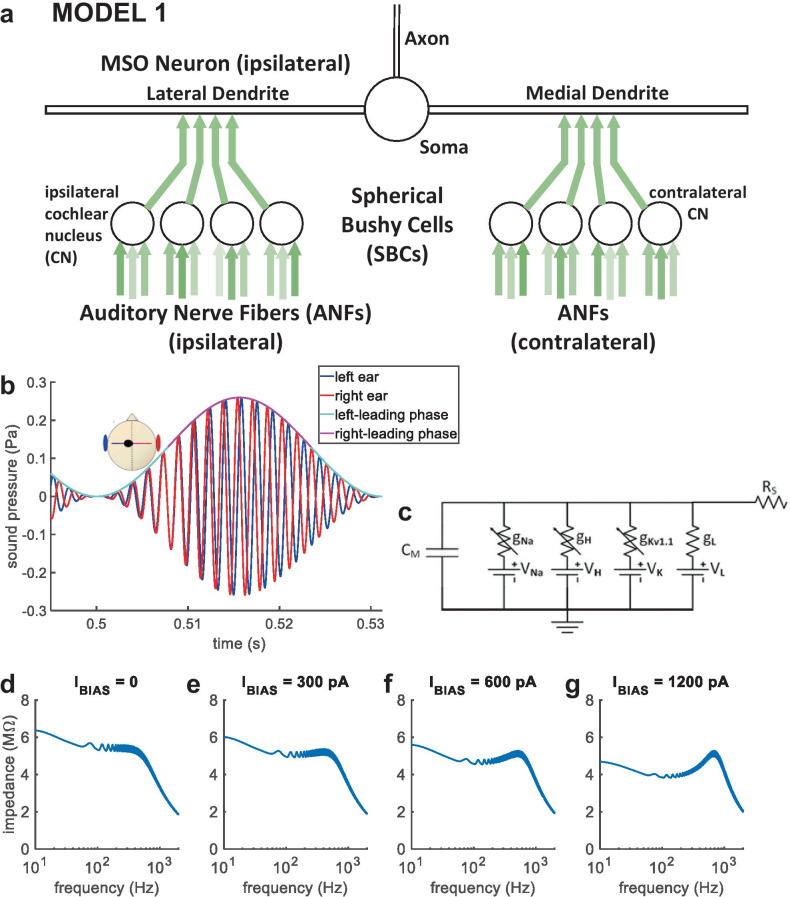
Fig. 2.
MODEL 1 and AMBB stimulus. (a) MODEL 1: nonlinear model for an MSO neuron and its excitatory inputs. (b) AMBB stimulus: AM rate is set equal to the binaural-beat frequency (the difference in carrier frequency between signals presented to the right and left ears); IPD cycles through 360° at the same rate as AM. The start-IPD (IPD at zero amplitude) is a free parameter. Shown with right-carrier 616 Hz, left-carrier 584 Hz, AM 32 Hz, and start-IPD −90° (right channel trailing by 90°), resulting in zero IPD at the midpoint of rising AM. (c) Sub-compartment within the model MSO neuron, shown as an electrical circuit. (d–g) Model MSO somatic membrane impedance vs. frequency. Injected current was a steady bias current (IBIAS), plus a frequency-swept sine wave. With increased IBIAS, a resonance in membrane impedance emerged. The reciprocal of angular resonance frequency indicates membrane time constant