Figure 1.
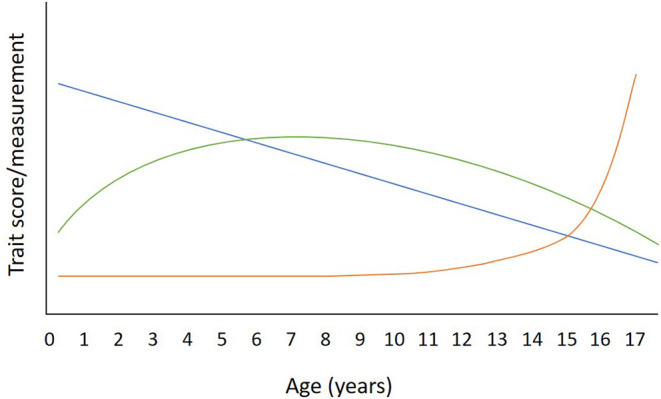
Illustrative example of three different types of relationships that behavioral traits could have with age in the dog. A linear relationship is illustrated in blue. An example of a trait that has a linear relationship with age would be activity/excitability, which peaks in puppyhood and declines steadily throughout the lifespan [e.g., (6)]. The Green arc illustrates a quadratic relationship, an example of which is attentiveness, which peaks in early adulthood and declines steadily thereafter [e.g., (7)]. The Orange line illustrates a trait that remains relatively stable until late life, when a steep change may be seen. An example of this trajectory is seen with the signs of canine cognitive dysfunction, which rises steadily from age 10 years, then rapidly after the age of 15 years (8).
