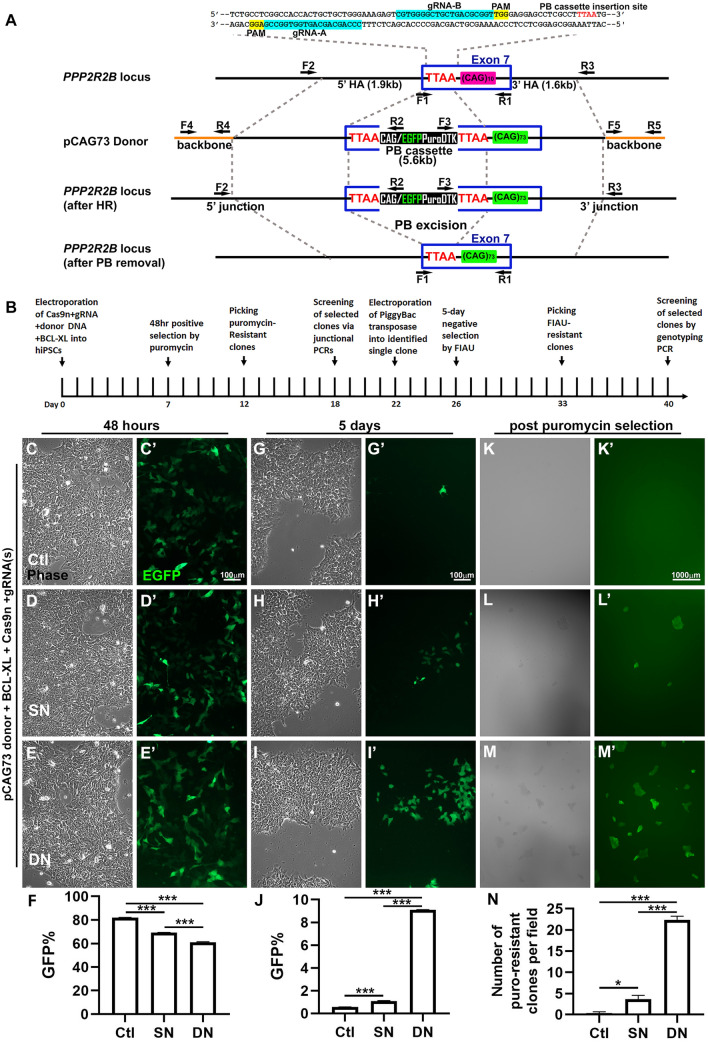
Figure 2.
Genome editing at the PPP2R2B locus in human iPSCs. (A) A schematic diagram (not drawn to scale) showing PPP2R2B exon 7, donor construct, PiggyBac (PB) selection cassette, and primer locations. HA: homologous arms; Puro: puromycin N-acetyltransferase gene; DTK: truncated thymidine kinase gene. EGFP/Puro/TDK was driven by the CMV early enhancer/chicken β actin (CAG) promoter. TTAA site was used for PB cassette insertion and removal. (B) Timeline of genome editing, including positive/negative selection, screening, excision, and rescreening. (C-N) GFP expression during the process of genome editing. GFP signal from the unincorporated donor is stable for up to five days post electroporation. GFP expression level was similar at 48 h post electroporation across control, SN, and DN conditions (C–F). EGFP declines rapidly in the control and was only marginally detected by day 5 (G–J’). Percentage of GFP positive cells in F and J was quantified by flow cytometry. N = 3 different wells of cells per condition. (F) One-way ANOVA F(2,6) = 1210; p < 0.001; Tukey’s multiple comparison test; ***p < 0.001. (J) One-way ANOVA F(2,6) = 19,852; p < 0.001; Tukey’s multiple comparison test; ***p < 0.001. (K–N)The number of GFP positive and puromycin resistant clones was substantially greater in cells following DN than following SN, or control treatment. Colony counting was performed at 2X magnification. N = 3 different fields per condition. Mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA F(2,6) = 253.1; p < 0.001; Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; ***p < 0.001.