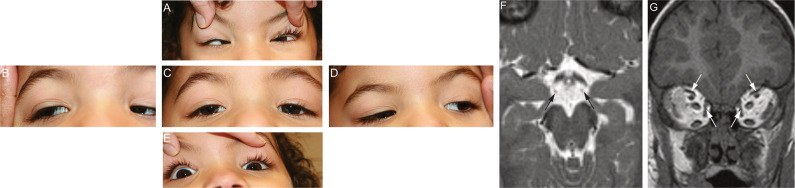
Fig. 1. TUBA1A variants are associated with CFEOM.
A–I Five positions of gaze in Individual 1 prior to her first strabismus surgery at 2.5 years of age, demonstrating ophthalmic features consistent with CFEOM. The individual’s eye movements were directed as follows: (A) up; (B) right; (C) forward; (D) left; (E) down. Notable ophthalmic features include: (A) bilateral limitations of upgaze and convergence on attempted upgaze; (C) Bilateral ptosis and primary eye position in downgaze; (B, D): full horizontal eye movements; (E): mild bilateral limitations of downgaze and preferred chin-up head positioning. F Axial T2 weighted MR image (2 mm/0 mm gap thickness) at the level of the interpeduncular and suprasellar cisterns faintly demonstrates the oculomotor nerves (arrows). Although the slice thickness was not optimized for cranial nerve imaging, these nerves appear hypoplastic. G Coronal T1 MPRAGE image (0.9 mm/0 mm gap thickness) through the orbits demonstrates small superior and medial rectus muscles bilaterally (arrows).