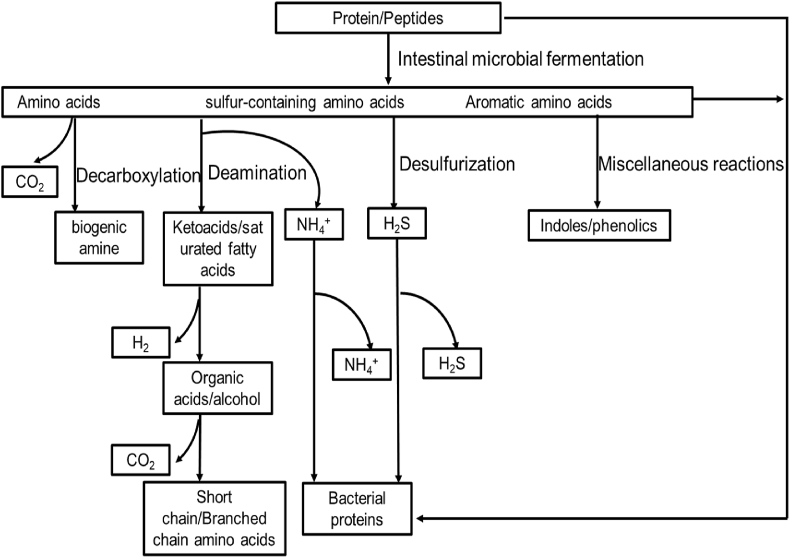
Fig. 1.
Protein catabolism pathway of colonic microorganisms. Amino acids produced by microbial metabolism can be directly used by microorganisms to synthesize bacterial protein, and can also enter the catabolic pathway, which is the primary metabolic mode of amino acids in the colon. In microbial metabolism, most amino acids produce corresponding ketoacids or saturated fatty acids through transamination or deamination such as short-chain fatty acids, organic acids, ethanol, H2, and CO2. Some amino acids are metabolized into biogenic amines by decarboxylation. Many complex amino acids, such as aromatic amino acids, do not occur only in the above general reactions. They can be metabolized by a series of reactions such as fission, deamination, decarboxylation, oxidation, and reduction to produce various indoles and phenols.