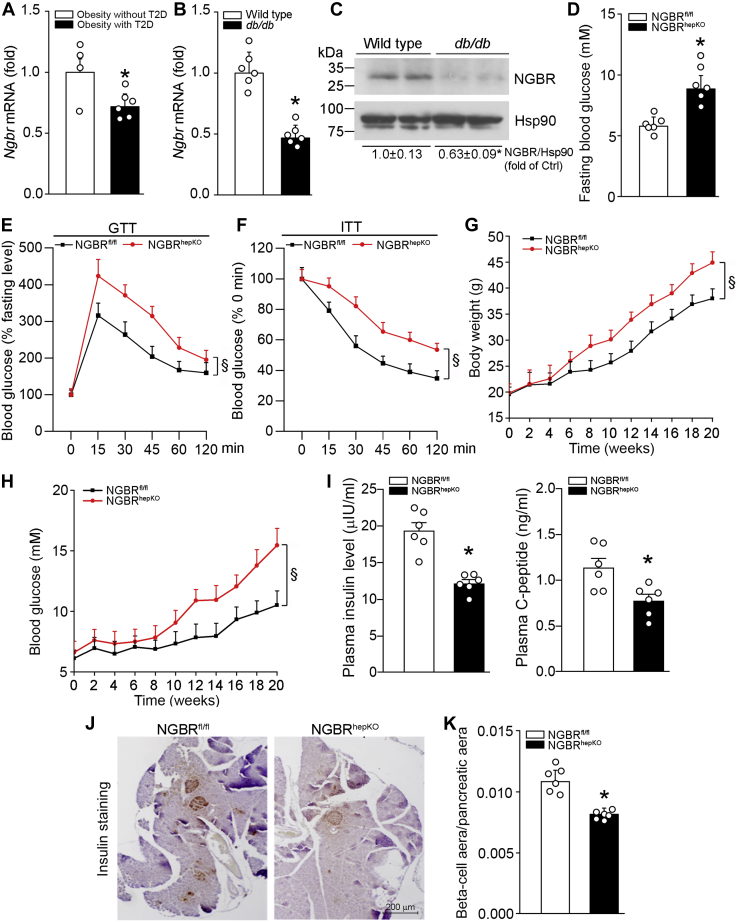
Figure 1.
Reduced NGBR expression in the liver is associated with insulin resistance and loss of pancreatic beta-cells.A, NGBR transcript level is decreased in T2D obese patients. The data is generated from NCBI gene expression omnibus database (GEO access: GSE15653) ∗p < 0.05. n = 4 (Obesity without T2D group), n = 6 (Obesity with T2D group). B and C, expression of NGBR mRNA and protein in the liver of wild-type and db/db mice was determined by qPCR and western blot analysis. ∗p < 0.05, n = 6. D, NGBRfl/fl and NGBRhepKO mice at 12-week-old were randomly divided into two groups (n = 6). Blood glucose levels were determined after 12 h fasting. ∗p < 0.05, n = 6. E, glucose tolerance test (GTT): blood glucose levels were determined at the indicated time points after i.p. injection of glucose (0.5 g/kg bodyweight). §p < 0.05, n = 6. F, insulin tolerance test (ITT): the mice were preadministrated glucose (0.5 g/kg bodyweight) for 2 h after 12-h fasting, then blood glucose levels were determined at the indicated time points after i.p. injection of insulin (1 U/kg bodyweight). §p < 0.05, n = 6. G and H, NGBRfl/fl and NGBRhepKO mice at 8-week-old were fed high-fat diet (HFD) for 20 weeks. Bodyweight and blood glucose were determined at the indicated time points. §p < 0.05, n = 6. I–K, 8-week-old mice were fed HFD for 4 weeks. Plasma was collected and levels of insulin and C-peptide were determined by ELISA kits (I). The mass of beta cells in the pancreas was determined by immunohistochemistry staining of the tissue sections with anti-insulin antibody, followed by quantitative analysis of the ratio of beta-cell area to pancreatic tissue area (J and K). Scale bar: 200 μm (J). ∗p < 0.05, n = 6.