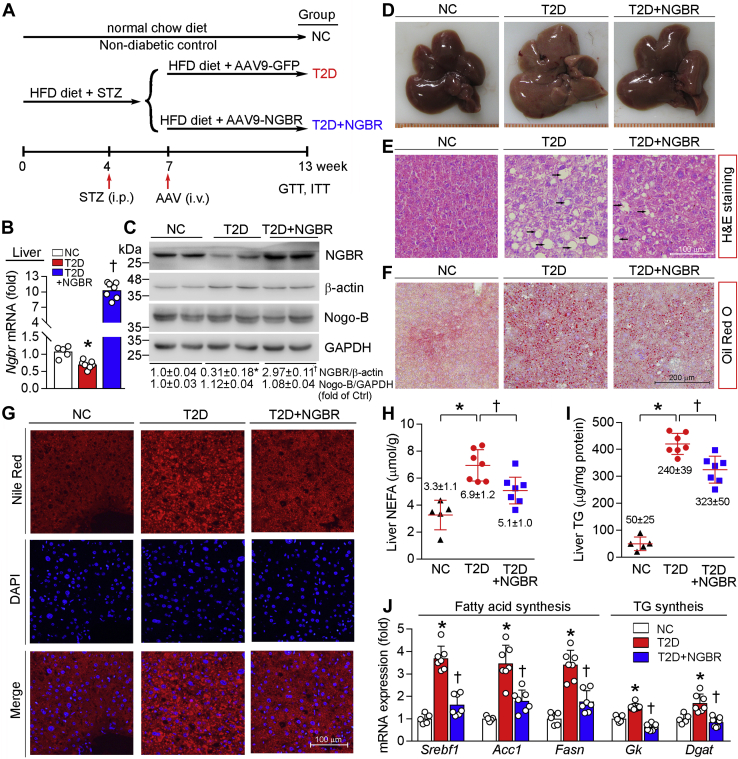
Figure 2.
Overexpression of hepatic NGBR attenuates high-fat diet (HFD)/streptozotocin (STZ)-induced hepatic lipid accumulation.A, experimental design: male C57BL/6 mice at 5-week-old were randomly divided in two groups and fed normal chow or HFD. Four weeks later, HFD-fed mice were fasted for 6 h and then i.p. injected STZ (50 mg day−1 kg−1 bodyweight) daily for seven consecutive days. Normal chow-fed mice were injected same volume of vehicle (citrate buffer) and used as negative control (NC). After confirming onset of diabetes (3 weeks after the first STZ injection), STZ-injected mice were further randomly divided into two groups, followed by i.v. injection of adeno-associated virus 9 (AAV9)-GFP or AAV9-NGBR once at a dose of 1 × 1012 vg/mouse, and named as T2D group and T2D+NGBR group, respectively. B–J, at the end of experiment, mouse liver samples were used to conduct the following assays. Hepatic Ngbr mRNA was determined by qPCR (B). NGBR and Nogo-B protein expression was determined by western blot (C). Liver photograph (D). H&E, Oil red O, and Nile red staining of liver frozen sections (E–G). Black arrows indicate the vacuoles of lipid droplets (E). Scale bar: 100 μm (E and G), 200 μm (F). Hepatic nonesterified fatty acid (NEFA) and triglyceride (TG) levels were determined with total lipid extract from a piece of liver using corresponding assay kits and normalized to liver protein content (H and I). mRNA expression profiles in NC, T2D, and T2D+NGBR mouse liver including genes related to fatty acid synthesis: sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 (Srebf1), acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (Acc1) and fatty acid synthase (Fasn), and TG synthesis: glycerol kinase (Gk) and diacylglycerol acyltransferase (Dgat), were determined by qPCR (J). ∗p < 0.05 versus NC; †p < 0.05 versus T2D. n = 5 (NC group), n = 7 (T2D or T2D+NGBR group).