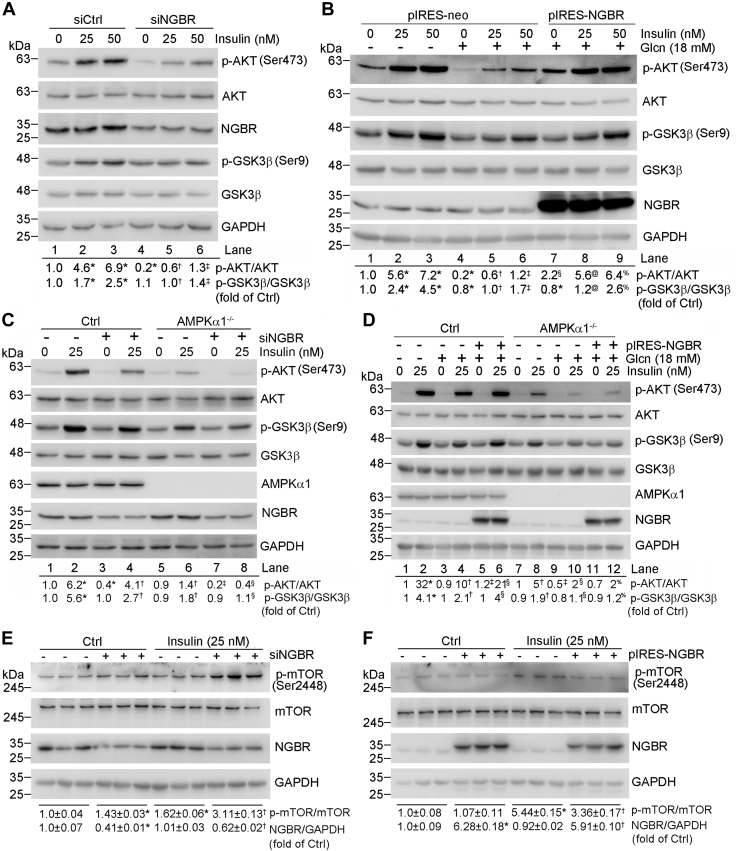
Figure 4.
NGBR regulates insulin sensitivity through insulin signaling, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) axis, and inhibiting mTOR in HepG2 cells.A and C, HepG2 cells (A) or HepG2-Ctrl cells and HepG2-AMPKα1−/− cells (C) in 6-well plates were transfected with scrambled siRNA (siCtrl, 50 nM) or NGBR siRNA (siNGBR, 50 nM) for 24 h. Cells were then treated with insulin at the indicated concentrations for 30 min. B and D, HepG2 cells (B) or HepG2-Ctrl cells and AMPKα1−/− cells (D) in 6-well plates were transfected with NGBR expression vector (pIRES-NGBR, 1 μg/well) or empty vector (pIRES-neo, 1 μg/well) for 12 h. Cells were then pretreated with glucosamine hydrochloride (Glcn) (18 mM) for 18 h, followed by insulin treatment for 30 min at the indicated concentrations. E, HepG2 cells in 6-well plates were transfected with scrambled siRNA (siCtrl, 50 nM) or NGBR siRNA (siNGBR, 50 nM) for 24 h. Cells were then treated with insulin (25 nM) for 30 min. F, HepG2 cells in 6-well plates were transfected with NGBR expression vector (pIRES-NGBR, 1 μg/well) or empty vector (pIRES-neo, 1 μg/well) for 12 h. Cells were then treated with insulin (25 nM) for 30 min. Expression of indicated proteins was determined by western blot. ∗p < 0.05 versus lane 1, siCtrl or pIRES-neo; †p < 0.05 versus lane 2, siNGBR or pIRES-NGBR; ‡p < 0.05 versus lane 3; §p < 0.05 versus lane 4; @p < 0.05 versus lane 5; %p < 0.05 versus lane 6. n = 3.