Figure 3. BRD4 Controls Transcriptional Responses In Vascular and Inflammatory Cells.
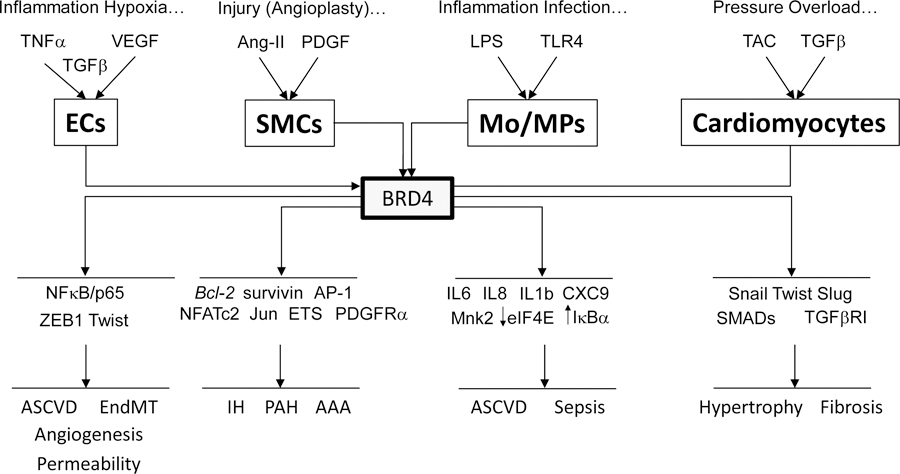
Examples of stimuli, regulated gene targets and pathologic responses involving specifically BRD4 in ECs, SMCs, monocyte/macrophages (Mo/MPs) and cardiomyocytes as reviewed here are shown. These BRD4 effects have been demonstrated through the use of gene expression, BETi responses and global profiling tools of RNA-Seq and/or ChIP-Seq. This data reveals BRD4 exerts broad, integrated transcriptional effects executed in large through its association with super enhancer regions to determine functional cellular responses and associated disease states. An example that supports BET action as directing transcriptional programs to achieve a coordinated output is evident in BET inhibition repressing NFκB-directed gene expression while concurrently increasing translation of IκBα, which also decreases NFκB activity. BRD2 and BRD3 have also been implicated in similar although often distinct responses relevant to the vasculature. Abbreviations, references as per text.
